(English Medium)
Academic Year: 2015-2016
Date & Time: 21st March 2016, 11:00 am
Duration: 2h
Advertisements
1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately.
2. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes.
This time is to be spent in reading the question paper.
3. The time given at the head of the paper is the time allowed for writing the answers.
4. Attempt all questions from Section I and any four questions from Section II.
The exchange of chromatid parts between the maternal and the paternal chromatids of a pair of homologous chromosomes during meiosis.
Chapter: [0.012] Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Structure of Chromosomes
The number of individuals inhabiting per unit area.
Chapter: [0.04] Population
The immunity acquired by providing readymade antibodies from outside for treating certain infectious diseases.
Chapter: [0.071] Health Organisations
The pollutants that cannot be broken down to simple and harmless products.
Chapter: [0.06] Pollution
The part of the brain that carries impulses from one hemisphere of the cerebellum to the other.
Chapter: [0.033] Nervous System and Sense Organs
A plant cell may burst when :
Turgor pressure equalises wall pressure.
Turgor pressure exceeds wall pressure.
Wall pressure exceeds turgor pressure.
None of the above
Chapter: [0.021] Absorption by Roots: The Processes Involved
The individual flattened stacks of membranous structures inside the chloroplasts are known as :
A. Grana
B. Stroma
C. Thylakoids
D. Cristae
Chapter: [0.023] Photosynthesis: Provider of Food for All [0.023] Photosynthesis: Provider of Food for All
The nephrons discharge their urine at ______.
Urinary bladder
Ureter
Renal pelvis
Renal pyramid
Chapter: [0.032] The Excretory System (Elimination of Body Wastes)
Gigantism and Acromegaly are due to :
A. Hyposecretion of Thyroxine
B. Hyposecretion of Growth hormone
C. Hypersecretion of Thyroxine
D. Hypersecretion of Growth hormone
Chapter: [0.034] The Endocrine System
The mineral ion needed for the formation of blood clot is :
A. Potassium
B. Sodium
C. Calcium
D. Iron
Chapter: [0.031] The Circulatory System
find odd one from following: Sewage, newspaper, Styrofoam, Hay.
Chapter: [0.06] Pollution
find odd one from following: Thymine, Cytosine, Adenine, Pepsin.
Chapter: [0.035] The Reproductive System
find odd one from following: Malleus, iris, Stapes, Incus.
Chapter: [0.033] Nervous System and Sense Organs [0.034] Sense Organs
find odd one from following: Cortisone, Somatotropin, Adrenocorticotropic hormone, Vasopression.
Chapter: [0.033] Nervous System and Sense Organs
find odd one from following: Typhoid, Haemophilia, Albinism, Colour blindness.
Chapter: [0.013000000000000001] Genetics – Some Basic Fundamentals
_____________ secreted by the (ii) _____________ lobe of the pituitary gland. If this hormone secretion is reduced, there is an increased production of urine. This disorder is called (iii) ____________. Sometimes excess glucose is passed with urine due to hyposecretion of another hormone called (iv) _____________ leading to the cause of a disease called (v) ______________.
Chapter: [0.032] The Excretory System (Elimination of Body Wastes)
State the exact location of the Centromere
Chapter: [0.012] Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Structure of Chromosomes [0.013000000000000001] Genetics – Some Basic Fundamentals
Advertisements
State the exact location of the Chordae tendinae
Chapter: [0.031] The Circulatory System
State the exact location of the Thyroid gland.
Chapter: [0.034] The Endocrine System
State the exact location of the Ciliary body
Chapter: [0.033] Nervous System and Sense Organs [0.034] Sense Organs
State the exact location of the Proximal convoluted tubule.
Chapter: [0.035] The Reproductive System
Given below is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye, study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
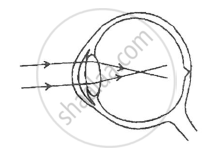
(i) Name the defect shown in the diagram.
(ii) What are the two possible that cause this defect?
(iii) Name the type of lens used to correct this defect.
(iv) With the help of a diagram show how the defect shown above is rectified using a suitable lens.
Chapter: [0.033] Nervous System and Sense Organs [0.034] Sense Organs
Given in the box below are a set of 14 biological terms. Of these, 12 can be paired into 6 matching pairs. Out of the six pairs, one has been done for you as an example.
Example : endosmosis - Turgid cell.
Identify the remaining five matching pairs :
| Cushing’s syndrome, Turgid cell, Iris, Free of rod and cone cells, Colour of eyes, Hypoglycemia, Active transport, Acrosome, Addison’s disease, Blind spot, Hyperglycemia, Spermatozoa, Endosmosis, Clotting of blood. |
Chapter: [0.033] Nervous System and Sense Organs [0.034] Sense Organs
State the main function of the Lymphocytes of blood
Chapter: [0.031] The Circulatory System
State the main function of the Leydig cells
Chapter: [0.035] The Reproductive System
State the main function of the Guard cells
Chapter: [0.021] Absorption by Roots: The Processes Involved
State the main function of the Eustachian tube
Chapter: [0.033] Nervous System and Sense Organs [0.034] Sense Organs
Name the function of the following:
Corpus luteum
Chapter: [0.035] The Reproductive System
The figure given below is a diagrammatic representation of a part of the cross section of the root in the root hair zone. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow

(i) Name the parts indicated by the guidelines 1 to 4.
(ii) Which is the process that enables the passage of water from the soil into the root hair?
(iii) Name the pressure that is responsible for the movement of water in the direction indicated by the arrows. Define it.
(iv) Due to an excess of this pressure sometimes drops of water are found along the leaf margins of some plants especially in the early mornings. What is the phenomenon called?
(v) Draw a well labelled diagram of the root hair cell as it would appear if an excess of fertiliser is added to the soil close to it.
Chapter: [0.021] Absorption by Roots: The Processes Involved
Differentiate between Human skin cell and Human ovum (number of chromosomes).
Chapter: [0.035] The Reproductive System
Differentiate between Sperm duct and fallopian rube (function)
Chapter: [0.035] The Reproductive System
Differentiate between Red Cross and WHO (one activity)
Chapter: [0.071] Health Organisations
Differentiate between Rod cells and cone cells (pigment)
Chapter: [0.035] The Reproductive System
Differentiate between LUBB and DUP (names of the valves whose closure produce the sound)
Chapter: [0.031] The Circulatory System
Given below is the outline of the human body showing the important glands :
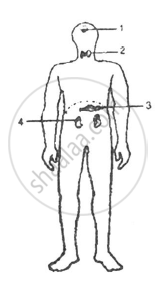
(i) Name the glands marked 1 to 4.
(ii) Name the hormone secreted by part 2. Give one important function of this hormone.
(iii) Name the endocrine part of the numbered 3.
(iv) Why is the part labelled I called the master gland? Which part of the forebrain controls the gland labelled I?
(v) Name the gland that secretes the ‘emergency hormone’.
Chapter: [0.034] The Endocrine System
Advertisements
The diagram of an given below demonstrates a particular process in plants. Study the same and answer the questions that follow :

(i) Name the apparatus.
(ii) Which phenomenon is demonstrated by this apparatus?
(iii) Explain the phenomenon mentioned in (ii) above.
(iv) State two limitations of using this apparatus.
(v) What is the importance of the air bubble in the experiment?
(vi) Name the structures in a plant through which the above process takes place.
Chapter: [0.021] Absorption by Roots: The Processes Involved
(i) Draw a well labelled diagram of the membranous labyrinth found in the inner ear.
(ii) Based on the diagram drawn above in (i) give a suitable term for each of the following descriptions :
1. The sensory cells that helps in hearing.
2. The part that is responsible for static balance of the body.
3. The membrane covered opening that connects the middle ear to the inner ear.
4. The fluid present in the middle chamber of cochlea.
5. The structure that maintains dynamic equilibrium of the body.
Chapter: [0.033] Nervous System and Sense Organs [0.034] Sense Organs
the Biological/technical term for Complete stoppage of menstrual cycle in females
Chapter: [0.035] The Reproductive System
the Biological/technical term Pigment providing colour to urine.
Chapter: [0.032] The Excretory System (Elimination of Body Wastes)
the Biological/technical term for The vein which drains the blood from the intestine to the liver.
Chapter: [0.031] The Circulatory System
the Biological/technical term for The canal through which the testes descend into the scrotum just before the birth of a male baby
Chapter: [0.035] The Reproductive System
The Biological/technical term for The process causing an undesirable change in the environment
Chapter: [0.06] Pollution
The Biological/technical term for The removal of nitrogenous wastes from the body
Chapter: [0.032] The Excretory System (Elimination of Body Wastes)
the Biological/technical term for The repeating components of each DNA strand lengthwise
Chapter: [0.013000000000000001] Genetics – Some Basic Fundamentals
the Biological/technical term for An alteration in the genetic material that can be inherited.
Chapter: [0.013000000000000001] Genetics – Some Basic Fundamentals
The Biological/technical term for The process of uptake of mineral ions against the concentration gradient using energy from the cell
Chapter: [0.021] Absorption by Roots: The Processes Involved
the Biological/technical term for Blood vessels carrying blood to the left atrium.
Chapter: [0.031] The Circulatory System
The given diagram shows a stage during mitotic division in an animal cell

(i) Identify the stage. Give a reason to support your answer.
(ii) Draw a neat labelled diagram of the cell as it would appear in the next stage. Name the stage.
(iii) In what two ways is mitotic division in an animal cell different from the mitotic division in a plant cell?
(iv) Name the type of cell division that occurs during :
A. Growth of a shoot
B. Formation of pollen grains.
Chapter: [0.012] Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Structure of Chromosomes
Give scientific reasons : Colour blindness is more common in men than in women.
Chapter: [0.013000000000000001] Genetics – Some Basic Fundamentals
Give scientific reasons: Injury to medulla oblongata leads to death.
Chapter: [0.071] Health Organisations
Give scientific reasons: When an ovum gets fertilized, menstrual cycle stops temporarily in a woman.
Chapter: [0.035] The Reproductive System
Give scientific reasons: Mature erythrocytes in humans lack nucleus and mitochondria
Chapter: [0.035] The Reproductive System
Give scientific reasons: Blood flows in arteries in spurts and is under pressure.
Chapter: [0.031] The Circulatory System
The diagram given below is that of a developing human foetus. Study the diagram and then answer the questions that follow:

(i) Label the parts numbered 1 to 3 in the diagram.
(ii) Mention any two functions of the part labelled 2 in the diagram.
(iii) Explain the significance of the part numbered 3 in the diagram.
(iv) Define the term ‘Gestation’. What is the normal gestational period of the developing human embryo?
(v) Mention the sex chromosomes in a male and female embryo.
Chapter: [0.035] The Reproductive System
The following diagram demonstrates a physiological process taking place in green plants. The whole set up was placed in bright sunlight for several hours. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow

(i) What aspect of the physiological process is being examined?
(ii) Explain the physiological process mentioned in (i) above.
(iii) Label the parts numbered 1 and 2 in the diagram.
(iv) Write a well-balanced chemical equation for the physiological process explained in (ii) above.
(v) What would happen to the rate of bubbling of the gas if a pinch of sodium bicarbonate is added to the water in the beaker? Explain your answer.
Chapter: [0.023] Photosynthesis: Provider of Food for All [0.023] Photosynthesis: Provider of Food for All
A homozygous tall plant (T) bearing red coloured (R) flowers is crossed with a homozygous dwarf (t) plant bearing white (r) flowers :-
(i) Give the genotype and phenotype of the plants of F1 generation.
(ii) Mention the possible combinations of the gametes that can be obtained from the F1 hybrid plant.
(iii) State the Mendel’s law of Independent Assortment.
(iv) Mention the phenotypes of the off springs obtained in F2 generation.
(v) What is the phenotypic ratio obtained in F2 generation?
Chapter: [0.013000000000000001] Genetics – Some Basic Fundamentals
Briefly explain the following terms : Reflex action
Chapter: [0.033] Nervous System and Sense Organs
Briefly explain the following terms: Power of accommodation
Chapter: [0.033] Nervous System and Sense Organs [0.034] Sense Organs
Briefly explain the following terms: Photophosphorylation
Chapter: [0.023] Photosynthesis: Provider of Food for All [0.023] Photosynthesis: Provider of Food for All
Briefly explain the following terms: Hormone
Chapter: [0.034] The Endocrine System
Briefly explain the following terms: Synapse
Chapter: [0.033] Nervous System and Sense Organs
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CISCE previous year question papers ICSE Class 10 Biology with solutions 2015 - 2016
Previous year Question paper for CISCE ICSE Class 10 -2016 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Biology, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CISCE ICSE Class 10 .
How CISCE ICSE Class 10 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Biology will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
