Advertisements
Advertisements
Two projectiles A and B are projected with angle of projection 15° for the projectile A and 45° for the projectile B. If RA and RB be the horizontal range for the two projectiles, then
Concept: undefined > undefined
A particle moves along the X-axis as x = u (t − 2 s) + a (t − 2 s)2.
(a) the initial velocity of the particle is u
(b) the acceleration of the particle is a
(c) the acceleration of the particle is 2a
(d) at t = 2 s particle is at the origin.
Concept: undefined > undefined
Advertisements
The geostationary orbit of the earth is at a distance of about 36000 km from the earth's surface. Find the weight of a 120-kg equipment placed in a geostationary satellite. The radius of the earth is 6400 km.
Concept: undefined > undefined
A man has to go 50 m due north, 40 m due east and 20 m due south to reach a field. (a) What distance he has to walk to reach the field? (b) What is his displacement from his house to the field?
Concept: undefined > undefined
A particle starts from the origin, goes along the X-axis to the point (20 m, 0) and then return along the same line to the point (−20 m, 0). Find the distance and displacement of the particle during the trip.
Concept: undefined > undefined
In the following figure Shows the graph of velocity versus time for a particle going along the X-axis. Find the acceleration
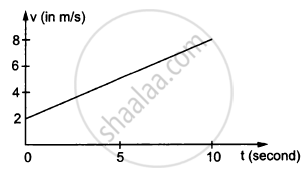
Concept: undefined > undefined
In the following figure Shows the graph of velocity versus time for a particle going along the X-axis. Find the distance travelled in 0 to 10s
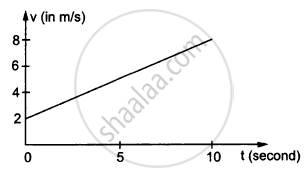
Concept: undefined > undefined
In the following figure Shows the graph of velocity versus time for a particle going along the X-axis. Find the displacement in 0 to 10 s.
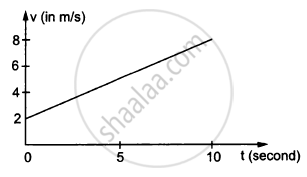
Concept: undefined > undefined
When you lift a box from the floor and put it on an almirah the potential energy of the box increases, but there is no change in its kinetic energy. Is it a violation of conservation of energy?
Concept: undefined > undefined
A particle is released from the top of an incline of height h. Does the kinetic energy of the particle at the bottom of the incline depend on the angle of incline? Do you need any more information to answer this question in Yes or No?
Concept: undefined > undefined
Can the work by kinetic friction on an object be positive? Zero?
Concept: undefined > undefined
Can static friction do nonzero work on an object? If yes, give an example. If no, give reason.
Concept: undefined > undefined
Can normal force do nonzero work on an object? If yes, give an example. If no, give reason.
Concept: undefined > undefined
Two springs A and B(kA = 2kB) are stretched by applying forces of equal magnitudes a the four ends. If the energy stored in A is E, that in B isA
Concept: undefined > undefined
In the Following figure shows the elliptical path of a planet about the sun. The two shaded parts have equal area. If t1 and t2 be the time taken by the planet to go from a to b and from c to d respectively,
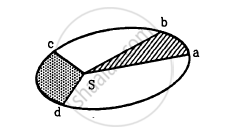
Concept: undefined > undefined
A person goes to bed at sharp 10.00 pm every day. Is it an example of periodic motion? If yes, what is the time period? If no, why?
Concept: undefined > undefined
If someone presses a pointed needle against your skin, you are hurt. But if someone presses a rod against your skin with the same force, you easily tolerate. Explain.
Concept: undefined > undefined
The total mechanical energy of a spring-mass system in simple harmonic motion is \[E = \frac{1}{2}m \omega^2 A^2 .\] Suppose the oscillating particle is replaced by another particle of double the mass while the amplitude A remains the same. The new mechanical energy will
Concept: undefined > undefined
A particle executes simple harmonic motion with a frequency v. The frequency with which the kinetic energy oscillates is
Concept: undefined > undefined
A particle executes simple harmonic motion under the restoring force provided by a spring. The time period is T. If the spring is divided in two equal parts and one part is used to continue the simple harmonic motion, the time period will
Concept: undefined > undefined
