Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: p-Block Elements - I
3: p-Block Elements - II
4: Transition and Inner Transition Elements
5: Coordination Chemistry
6: Solid State
7: Chemical Kinetics
8: Ionic Equilibrium
9: Electro Chemistry
10: Surface Chemistry
11: Hydroxy Compounds and Ethers
▶ 12: Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids
13: Organic Nitrogen Compounds
14: Biomolecules
15: Chemistry in Everyday Life
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 12 - Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 12 - Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-volume-1-and-2-english-class-12-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 12: Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 12 of Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Samacheer Kalvi for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board.
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board 12 Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids Evaluation [Pages 189 - 194]
Choose the correct answer:
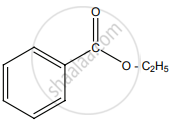
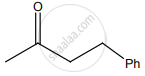
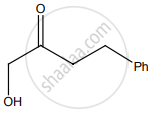
The correct structure of the product ‘A’ formed in the reaction is
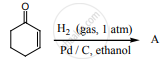
The formation of cyanohydrin from acetone is an example of ____________.
nucleophilic substitution
electrophilic substitution
electrophilic addition
nucleophilic addition
Reaction of acetone with one of the following reagents involves nucleophilic addition followed by elimination of water. The reagent is:
Grignard reagent
Sn/HCl
hydrazine in presence of slightly acidic solution
hydrocyanic acid
In the following reaction,
\[\ce{HC ≡ CH ->[H2SO4][HgSO4] X}\]
Product ‘X’ will not give
Tollen’s test
Victor Meyer test
Iodoform test
Fehling solution test
\[\ce{CH2 = CH2 ->[i) O3][ii) Zn/H2O] X ->[NH3] Y}\] ‘Y’ is:
Formaldehyde
di acetone ammonia
hexamethylene tetraamine
oxime
Predict the product Z in the following series of reactions.
\[\ce{Ethanoic acid ->[PCl5] X ->[C6H6][Anhydrous AlCl3] Y ->[i) CH3MgBr][H3O^+] Z}\]
(CH3)2C(OH)C6H5
CH3CH(OH)C6H5
CH3CH(OH)CH2 – CH3
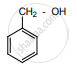
Assertion: 2, 2-dimethyl propanoic acid does not give HVZ reaction.
Reason: 2-2, dimethyl propanoic acid does not have α-hydrogen atom.
if both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
if both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
assertion is true but reason is false.
both assertion and reason are false.
Which of the following represents the correct order of acidity in the given compounds.
FCH2COOH > CH3COOH > BrCH2COOH > ClCH2COOH
FCH2COOH > ClCH2COOH > BrCH2COOH > CH3COOH
CH3COOH > ClCH2COOH > FCH2COOH > Br-CH2COOH
ClCH2COOH > CH3COOH > BrCH2COOH > ICH2COOH
\[\ce{Benzoic acid ->[i) NH3][ii) \Delta] A ->[NaOBr] B ->[NaNO2/HCl] C}\] ‘C’ is:
anilinium chloride
O-nitro aniline
benzene diazonium chloride
m-nitro benzoic acid
\[\ce{Ethanoic acid ->[P/Br2] 2-bromoethanoic acid}\]. This reaction is called ____________.
Finkelstein reaction
Haloform reaction
Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction
None of these
\[\ce{CH3Br ->[KNC] (A) ->[H3O^+] (B) ->[PCl5] (C)}\] product (C) is:
acetyl chloride
chloro acetic acid
α-chlorocyano ethanoic acid
none of these
Which one of the following reduces tollens reagent.
formic acid
acetic acid
benzophenone
none of these
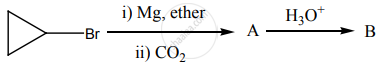
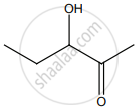
‘B’ is:
The IUPAC name of
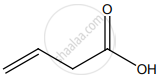
but-3-enoic acid
but-1-ene-4-oic acid
but-2-ene-1-oic acid
but-3-ene-1-oic acid
Identify the product formed in the reaction.
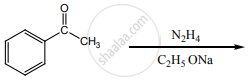
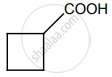
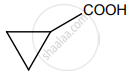
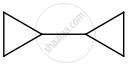
In which case, chiral carbon is not generated by reaction with HCN.
Assertion: p-N, N-dimethyl amino benzaldehyde undergoes benzoin condensation
Reason: The aldehydic (−CHO) group is meta directing.
if both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
if both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
assertion is true but reason is false.
both assertion and reason are false.
Which one of the following reaction is an example of disproportionation reaction.
Aldol condensation
Cannizaro reaction
Benzoin condensation
None of these
Which one of the following undergoes reaction with 50% sodium hydroxide solution to give the corresponding alcohol and acid.
Phenylmethanal
ethanal
ethanol
methanol
The reagent used to distinguish between acetaldehyde and benzaldehyde is ____________.
Tollens reagent
Fehling’s solution
2, 4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine
semicarbazide
Phenyl methanal is reacted with concentrated NaOH to give two products X and Y. X reacts with metallic sodium to liberate hydrogen X and Y are ____________.
sodium benzoate and phenol
sodium benzoate and phenyl methanol
phenyl methanol and sodium benzoate
none of these
In which of the following reactions new carbon-carbon bond is not formed?
Aldol condensation
Friedel craft reaction
Kolbe’s reaction
Wolf kishner reduction
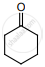
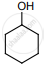
An alkene “A” on reaction with O3 and Zn – H2O gives propanone and ethanol in equimolar ratio. Addition of HCl to alkene “A” gives “B” as the major product. The structure of product “B” is
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{....................}\ce{CH3}\\
\phantom{.................}|\\
\ce{Cl - CH2 - CH2 - CH}\\
\phantom{.................}|\\
\phantom{....................}\ce{CH3}
\end{array}\]\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..........}\ce{CH2Cl}\\
\phantom{.....}|\\
\ce{H3C - CH2 - CH - CH3}
\end{array}\]\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.........}\ce{CH3}\\
\phantom{.......}|\\
\ce{H3C - CH2 - C - CH3}\\
\phantom{.......}|\\
\phantom{........}\ce{Cl}
\end{array}\]\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..............}\ce{CH3}\\
\phantom{............}|\\
\ce{H3C - CH - CH}\\
\phantom{............}|\\
\phantom{............}\ce{Cl}
\end{array}\]
Carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular mass. It is due to their ____________.
more extensive association of carboxylic acid via van der Waals force of attraction
formation of carboxylate ion
formation of intramolecular H-bonding
formation of intermolecular H-bonding
Short Answer Questions:
How is propanoic acid is prepared to start from alcohol?
How is propanoic acid is prepared to start from an alkyl halide?
How is propanoic acid is prepared to start from an alkene?
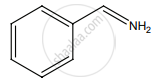
A Compound (A) with molecular formula C2H3N on acid hydrolysis gives (B) which reacts with thionyl chloride to give compound (C). Benzene reacts with compound (C) in presence of anhydrous AlCl3 to give compound (D). Compound (D) on reduction with Zn/Hg and Conc. HCl gives (E). Identify (A), (B), (C), (D) and (E). Write the equations.
Identify X and Y.
\[\ce{CH3COCH2CH2COOC2H5 ->[CH3MgBr] X ->[H3O^+] Y}\]
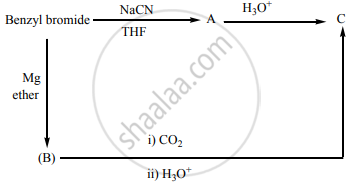
Identify A, B and C.
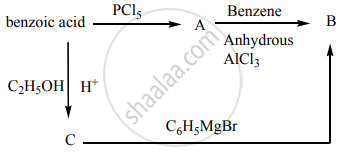
Identify A, B, C and D.
\[\ce{ethanoic acid ->[SOCl2] A ->[Pd/BaSO4] B ->[NaOH] C ->[][\Delta] D}\]
An alkene (A) on ozonolysis gives propanone and aldehyde (B). When (B) is oxidised (C) is obtained. (C) is treated with Br2/P gives (D) which on hydrolysis gives (E). When propanone is treated with HCN followed by hydrolysis gives (E). Identify A, B, C, D and E.
How will you convert benzaldehyde into the following compound?
Benzophenone
How will you convert benzaldehyde into the following compound?
Benzoic acid
How will you convert benzaldehyde into the following compound?
α-hydroxy phenyl acetic acid
What is the action of HCN on propanone?
What is the action of HCN on 2, 4-dichlorobenzaldehyde?
What is the action of HCN on ethanal?
A carbonyl compound A having molecular formula C5H10O forms crystalline precipitate with sodium bisulphate and gives positive iodoform test. A does not reduce Fehling's solution. Identify A.
Write the structure of the major product of the aldol condensation of benzaldehyde with acetone.
How is the following conversion effected propanal into butanone?
How is the following conversion effected Hex-3-yne into hexan-3-one?
How is the following conversion effected phenyl methanal into benzoic acid?
How is the following conversion effected phenyl methanal into benzoin?
Complete the following reaction.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - CH2 - CH2 - C - CH3 ->[HO - CH2 - CH2 - CH2 - OH][dry HCl] ?}\\
||\phantom{.........}\\
\ce{O}\phantom{.........}
\end{array}\]
Identify A, B and C.
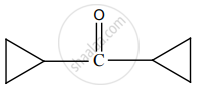
Oxidation of ketones involves carbon-carbon bond cleavage. Name the product(s) is/are formed on oxidising 2, 5-dimethyl hexan-3-one using a strong oxidising agent.
How will you prepare acetic anhydride from acetic acid?
How will you prepare ethyl acetate from methyl acetate?
How will you prepare acetamide from methyl cyanide?
How will you prepare lactic acid from ethanol?
How will you prepare acetophenone from acetyl chloride?
How will you prepare ethane from sodium acetate?
How will you prepare benzoic acid from toluene?
How will you prepare malachite green from benzaldehyde?
How will you prepare cinnamic acid from benzaldehyde?
How will you prepare acetaldehyde from ethyne?
Solutions for 12: Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 12 - Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 12 - Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-volume-1-and-2-english-class-12-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 12 - Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids
Shaalaa.com has the Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Mathematics Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education 12 (Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Samacheer Kalvi textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board chapter 12 Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids are Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones, Structure of Carbonyl Group, General Methods of Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones, Physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones, Chemical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones, Test for Aldehydes, Uses of Carboxylic Acids and Its Derivatives, Uses of Aldehydes and Ketones, IUPAC Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acids, Structure of the Carboxyl group, Methods of Preparation of Carboxylic Acids, Physical Properties of Carboxylic Acids, Chemical Properties of Carboxylic Acids, Acidity of Carboxylic Acids, Functional Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids.
Using Samacheer Kalvi Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board solutions Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Samacheer Kalvi Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board students prefer Samacheer Kalvi Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 12, Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board additional questions for Mathematics Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 12 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.