Topics
Reproduction
Reproduction in Organisms
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Introduction of Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Flower - a Fascinating Organ of Angiosperms
- Essential Parts of Flower: Androecium
- Development of Female Gametophytes
- Essential Parts of Flower: Gynoecium
- Pollination
- Fertilization Process
- Development of Endosperm
- Polyembryony
- Development of Male Gametophytes
- Significance of Seed Dispersal and Fruit Formation
Human Reproduction
- The Male Reproductive System
- Microscopic Anatomy of Testis
- Microscopic Anatomy of Ovary
- Gametogenesis
- Menstrual Cycle (Ovarian Cycle)
- Fertilization and Implantation
- Embryo Development Upto Blastocyst Formation
- Pregnancy and Embryonic Development
- Parturition and Lactation
Reproductive Health
Genetics and Evolution
Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Heredity and Variation
- Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity
- Extensions of Mendelian Genetics (Deviation from Mendelism)
- Polygenic Inheritance
- Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
- Sex Determination
- Sex Determination in Some Insects
- Linkage and Crossing Over
- Genetic Disorders
- Sex Determination in Birds
- Sex Determination in Honey Bees
Molecular Basis of Inheritance
Evolution
- Origin and Evolution of Universe and Earth
- Theories of Origin of Life
- Darwinism
- Evidences for Biological Evolution
- Adaptive Radiation
- Theories of Biological Evolution
- Micro and Macro Evolution
- Organic Evolution
- Speciation
- Hardy Weinberg’s Principle
- Evolution Stages
- Human Evolution
- Modern Synthetic Theory of Evolution
- Gene Flow and Genetic Drift
Biology and Human Welfare
Human Health and Diseases
- Introduction of Human Health and Diseases
- Infectious and Non Infectious Disease
- Maintaining Good Health, Yoga, Excercise
- Common Diseases in Human Beings
- Immunity
- Types of Immunity
- Interferons
- Antibodies
- Vaccination and Immunization
- Allergies (Hypersensitivity)
- Signs and Symptoms of Allergies
- Autoimmunity
- Lymphoid Organs
- Cancer
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)
- Adolescence - Drug and Alcohol Abuse
Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
Microbes in Human Welfare
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Microbes in Household Products
- Microbes in Industrial Production
- Microbes in Sewage Treatment
- Microbes in Production of Biogas
- Microbes as Biocontrol Agents
- Energy Generation
- Production and Judicious Use
Biotechnology and Its Applications
Biotechnology - Principles and Processes
- Process and Principles of Biotechnology
- Genetic Engineering (Recombinant DNA Technology).
Biotechnology and Its Applications
Ecology and Environment
Organisms and Populations
Ecosystem
- Introduction and Types of Ecosystem
- Structure and Function of an Ecosystem
- Productivity
- Decomposition
- Concept of Energy Flow in an Ecosystem
- Ecological Pyramids
- Ecological Succession
- Nutrient Cycles
- Ecosystem Services
- Ecosystems Patterns
Biodiversity and Its Conservation
- Biodiversity
- Patterns of Biodiversity
- Importance of Biodiversity
- Loss of Biodiversity
- Conservation of Biodiversity
- Endangered Organisms
- Extinction
- Red Data Book
Environmental Issues
- Environmental Issues
- Pollution
- Air Pollution and Its Causes
- Sources of Air Pollution
- Prevention of Air Pollution
- Noise Pollution
- Measures to Limit Noise Pollution
- Introduction of Water Pollution and Its Control
- Water Pollution and Its Causes
- Prevention of Water Pollution
- Composition of Waste Water
- Thermal Pollution
- Eutrophication
- Biochemical Oxygen Demand and Water
- A Case Study of Integrated Waste Water Treatment
- Soil Pollution and its Causes
- Effects of Soil Pollution
- Prevention of Soil Pollution
- Agrochemicals and Their Effects
- Integrated Organic Farming
- Biomagnification and Bioconcentration
- Solid Waste Management
- Radioactive Waste Management and E-waste
- Greenhouse Effect and Climate Change
- Ozone Depletion in the Stratosphere
- Deforestation and Its Causes
- Main Provisions of Environmental Acts
Definition
Asexual Reproduction in animals:
- The formation of progeny is by a single parent only and does not involve both the sexes, so it is called asexual reproduction.
- The progeny or daughter cells are genetically identical to the single parent and are also called clones.
Modes of asexual reproduction:
1. Gemmule Formation
- A gemmule is an internal bud found in sponges, consisting of asexually produced dormant cells called archaeocytes.
- These cells can develop into new organisms when coated by a thick layer of amoebocyte secretion.
- When favourable conditions return, the gemmule hatches and develops into a new organism, like sponges.
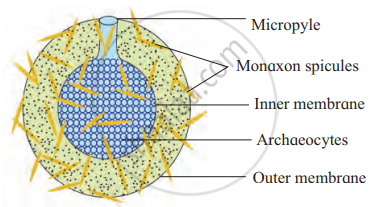
Gemmule
2. Budding
- It is a simple method, occuring in favorable conditions. In Hydra, a small outgrowth (bud) is produced towards the basal end of the body.
- It develops as a bud which grows and forms tentacles and develops (get transformed) into a new individual. This process is called budding.
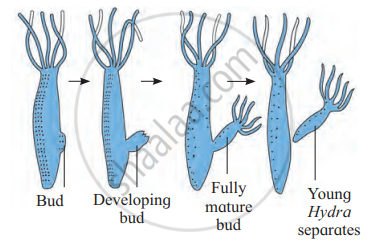
Budding in Hydra
3. Regeneration
- By this process, the organism can repair, regrow or restore its lost or damaged part. Though it involves asexual processes, it differs distinctly from reproduction, e.g., a damaged hydra can regenerate its lost part.
- Similarly, Planaria if wounded, its cells become active and regenerate lost part or organ back to its original state.
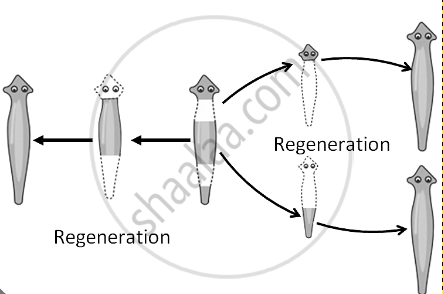
Regeneration in planaria
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
Video Tutorials
Shaalaa.com | Asexual Reproduction
to track your progress
