Carbon dioxide (CO₂) is a chemical compound consisting of molecules where one carbon atom is covalently double-bonded to two oxygen atoms. The molecular mass of CO₂ is 44 g/mol. It is an essential component of Earth's atmosphere and plays a significant role in various biological and chemical processes. CO₂ has a melting point of -56.6°C, indicating it transitions from solid to gas at very low temperatures under standard atmospheric conditions. At room temperature, it exists as a gas and is odourless at typical concentrations. As the primary carbon source for the carbon cycle, atmospheric CO₂ is essential for sustaining life on Earth. While transparent to visible light, carbon dioxide absorbs infrared radiation, contributing to its role as a greenhouse gas. It is also soluble in water and can be found in groundwater, lakes, ice caps, and seawater.
- Carbon dioxide is present in the air in a free state, constituting about 0.03% of the atmosphere. It is an essential greenhouse gas that helps regulate Earth's temperature.
- The air we exhale contains about 4% carbon dioxide, as it is a byproduct of respiration.
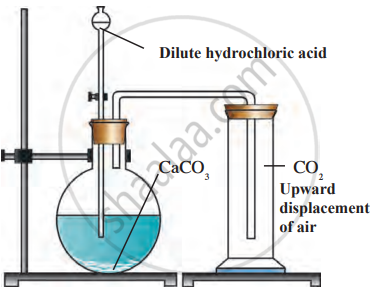
- Carbon dioxide is found in the form of salts, such as calcium carbonate, which is present in chalk, Shahabad tiles, marble, and limestone.
- CO₂ is released during the combustion of wood, fossil fuels like coal, and other organic materials. This process is a significant source of carbon dioxide in the environment.