Topics
Heredity and Evolution
- Heredity or Inheritance
- Protein Synthesis
- Transcription
- Translation
- Translocation
- Concept of Mutation
- Mutation Theory
- Evolution and Classiffication
- Evidences for Biological Evolution
- Darwinism
- Lamarck’s Theory of Evolution
- Speciation
- Human Evolution
Life Processes in Living Organisms Part -1
- Living Organisms and Life Processes
- Living Organisms and Energy Production
- Production of ATP
- Types of Respiration: Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
- Energy From Different Food Components
- Cell Division: an Essential Life Process
- Mitosis and Its Phases
- Phases of Mitosis: Karyokinesis (Division of Nucleus)
- Phases of Mitosis: Cytokinesis (Division of Cytoplasm)
- Significance of Mitosis
- Meiosis as a Reduction Division
- Stages of Meiosis: Meiosis I
- Stages of Meiosis: Meiosis II
- Significance of Meiosis
- Differences Between Mitosis and Meiosis
Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2
- Introduction to Life Processes in Living Organisms
- Reproduction
- Asexual Reproduction in Animal
- Fission
- Fragmentation
- Regeneration
- Budding
- Sporulation (Sporogenesis)
- Asexual Reproduction in Plant
- Budding
- Vegetative Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals
- Human Reproduction
- The Male Reproductive System
- The Female Reproductive System
- Gametogenesis
- Fertilization in Human
- Embryonic Development in Human
- Implantation in Human
- Pregnancy in Humans
- Placenta (Growth) in Human
- Parturition (Birth) in Human
- Menstrual Cycle (Ovarian Cycle)
- Reproduction and Modern Technology
- Reproductive Health
Environmental Management
- Our Needs and the Environment
- Ecosystem
- Relationship Between Environment and Ecosystem
- Environmental Balance
- Environmental Conservation
- Environmental Conservation and Biodiversity
- Classification of Threatened Species
Towards Green Energy
- Energy and Use of Energy
- Generation of Electrical Energy
- Power Plants Based on Thermal Energy
- Power Plants Based on Nuclear Energy
- Power Plants Based on Natural Gas
- Electric Energy Generation and Environment
- Electricity Generation using Hydroelectric Energy
- Electricity Generation using Wind Energy
- Electricity Generation using Solar Energy
Animal Classification
- Biological Classification
- Classification of Living Organisms
- History of Animal Classification
- Traditional Method of Animal Classification
- Conventional System of Animal Classification
- Criteria for New System of Classification
- Phylum: Porifera
- Phylum: Cnidaria/Coelenterata
- Phylum: Platyhelminthes
- Phylum: Aschelminthes
- Phylum: Annelida
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Phylum: Mollusca
- Phylum: Echinodermata
- Phylum: Hemichordata
- Phylum: Chordata
- Subphylum: Urochordata
- Subphylum: Cephalochordata
- Subphylum -Vertebrata/Craniata
- Class: Cyclostomata
- Class: Pisces
- Class: Amphibia
- Class: Reptilia
- Class: Aves
- Class: Mammalia
Introduction to Microbiology
- Microorganisms (Microbes) and Microbiology
- Introduction to Applied and Industrial Microbiology
- Useful micro-organisms
Cell Biology and Biotechnology
- Cell Biology (Cytology)
- Stem Cells
- Organ Transplantation
- Organ and Body Donation
- Biotechnology
- Commercial Applications of Biotechnology
- Modern Agricultural Practices and Crop Improvement
- Important Stages in Agricultural Development
Social Health
- Social Health
- Factors Disturbing the Social Health
- Communication Media and Excessive Use of Modern Technology
- Stress Management
Disaster Management
- Disaster
- Effects of Disaster
- Nature and Scope of Disaster
- Disaster Management
- Classification of Disaster Management
- Disaster Management Cycle
- Structure of Disaster Management Authority
- First Aid and Emergency Action
- Mock Drill
Life's Internal Secrets
The Regulators of Life
- Coordination in Plants - Introduction
- Control and Co-ordination in Plants
- Human Nervous System
- Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Chemical Control
The Life Cycle
Mapping Our Genes
Striving for Better Environment 2
- Use of Efficient and Eco-friendly Technology
- Sustainable Use of Resources
- Enforcement of Acts, Laws and Policies
Understanding Metals and Non-Metals
Amazing World of Carbon Compounds
- Introduction
- Hydroelectricity and its Production
- Application of Hydroelectric Energy
Introduction:
Hydroelectric energy, also called hydropower or water power, is a type of energy that comes from using moving water to create electricity. The word "hydropower" combines two words: hydro (meaning water) and power. So, it means getting power or electricity from water.
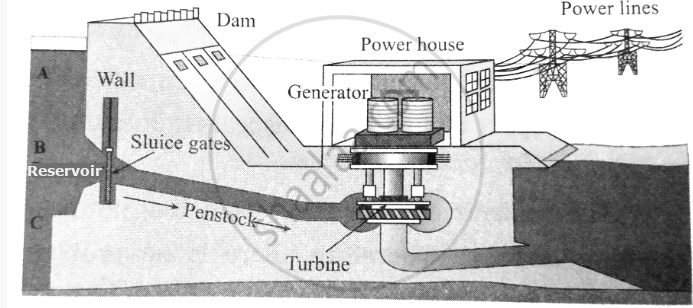
Working of Hydroelectric Energy
To produce hydroelectricity, we use falling or flowing water. This could be water from a river, waterfall, or even a dam. When water moves fast, it has kinetic energy (the energy of motion). This kinetic energy is captured and converted into electricity that we can use to power things like machines, lights, etc.
Hydroelectricity and its Production
Hydroelectricity is electricity that is created using hydropower. People have been using water to create energy for over 1,000 years! Today, hydroelectric energy provides about one-sixth of the world's electricity. That’s a lot of power! This energy is also renewable, which means it can be produced again and again as long as there is water.
Hydroelectricity is mostly produced by dams or diversion structures. Here's how it works:
- Building a Dam: First, we build a dam on a river to store water in a reservoir (a big storage area). The dam holds back the water, and when we need electricity, we release the water.
- Water Flows: When the water is released, it flows through pipes inside the dam. The flowing water has kinetic energy because it is moving.
- Turning a Turbine: Water flows through the pipe and hits a turbine, which is like a big wheel with blades. The force of the water spins the turbine.
- Generating Electricity: When the turbine spins, it turns a generator. The generator converts the kinetic energy of the water into electrical energy. This electricity can then be used to power homes, schools, and factories.
Application of Hydroelectric Energy:
- Hydroelectric energy is primarily used to produce electricity for homes, businesses, and industries. It powers millions of people worldwide.
- Hydroelectric plants help manage water flow, which is helpful in irrigating agricultural fields and ensuring crops get sufficient water.
- Dams used for hydroelectric power also help control floods by regulating water levels and protecting nearby communities.
- Dams and reservoirs created for hydroelectricity can also store water, providing clean drinking water for nearby towns and cities.
- Reservoirs created by dams offer recreational activities like boating and fishing, attracting tourists and supporting local economies.
