Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
50 m3 of saturated vapour is cooled down from 30°C to 20°C. Find the mass of the water condensed. The absolute humidity of saturated water vapour is 30 g m−3 at 30°C and 16 g m−3 at 20°C.
उत्तर
We Know that 1 `"m"^3` of air contains 30 g of water vapour at `30^circ`C.
So, amount of water vapour in 50 `"m"^3` of air at `30^circ`C = (`30 xx 50`) g = 1500 g
Also , 1 `"m"^3` of air contains 16 g of water vapour at `20^circ "C"`.
Amount of water vapour in 50 `"m"^3` of air at `20^circ`C. = `(16 xx 50)` g = 800 g
Amount of water vapour condensed = (1500 - 800) g = 700 g
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Molar volume is the volume occupied by 1 mol of any (ideal) gas at standard temperature and pressure (STP: 1 atmospheric pressure, 0 °C). Show that it is 22.4 litres
The figure shows the plot of PV/T versus Pfor 1.00×10–3 kg of oxygen gas at two different temperatures.
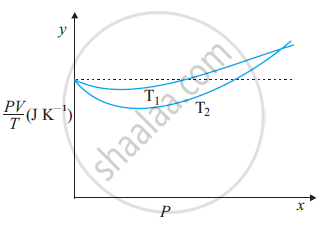
(a) What does the dotted plot signify?
(b) Which is true: T1 > T2 or T1 < T2?
(c) What is the value of PV/T where the curves meet on the y-axis?
(d) If we obtained similar plots for 1.00 ×10–3 kg of hydrogen, would we get the same value of PV/T at the point where the curves meet on the y-axis? If not, what mass of hydrogen yields the same value of PV/T (for low pressure high temperature region of the plot)? (Molecular mass of H2 = 2.02 u, of O2 = 32.0 u, R = 8.31 J mo1–1 K–1.)
An oxygen cylinder of volume 30 litres has an initial gauge pressure of 15 atm and a temperature of 27 °C. After some oxygen is withdrawn from the cylinder, the gauge pressure drops to 11 atm and its temperature drops to 17 °C. Estimate the mass of oxygen taken out of the cylinder (R = 8.31 J mol–1 K–1, molecular mass of O2 = 32 u)
At what temperature is the root mean square speed of an atom in an argon gas cylinder equal to the rms speed of a helium gas atom at – 20 °C? (atomic mass of Ar = 39.9 u, of He = 4.0 u).
What do you understand by gas?
A gas occupies 500 cm3 at a normal temperature. At what temperature will the volume of the gas be reduced by 20% of its original volume, the pressure is constant?
Name or state the following:
The standard pressure of a gas in cm. of mercury corresponding to one atmospheric pressure.
Name or state the following:
The absolute temperature value corresponding to 35°C.
The average energy per molecule is proportional to ______
If the absolute temperature of a body is doubled, the power radiated will increase by a factor of ______
Show that for monoatomic gas the ratio of the two specific heats is 5:3.
Show that for diatomic gas the ratio of the two specific heats is 7:5.
Gases exert pressure on the walls of the container because the gas molecules ______
Estimate the average thermal energy of a helium atom at the temperature on the surface of the Sun (6000 K).
Which of the following diagrams (Figure) depicts ideal gas behaviour?
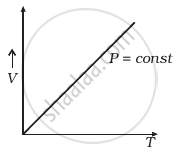 (a) |
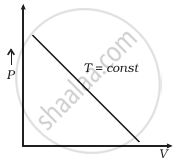 (b) |
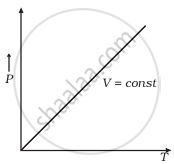 (c) |
 (d) |
The volume V of an enclosure contains a mixture of three gases, 16 g of oxygen, 28 g of nitrogen and 44 g of carbon dioxide at absolute temperature T. Consider R as universal gas constant. The pressure of the mixture of gases is ______.
Cooking gas containers are kept in a lorry moving with uniform speed. The temperature of the gas molecules inside will ______.
For a wave, y = 0.0002 sin`[2pi(110"t"-x/3)+pi/3]` is travelling in a medium. The energy per unit volume being transferred by wave if density of medium is 1.5 kg/m3, is ______.
