Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
50 m3 of saturated vapour is cooled down from 30°C to 20°C. Find the mass of the water condensed. The absolute humidity of saturated water vapour is 30 g m−3 at 30°C and 16 g m−3 at 20°C.
Solution
We Know that 1 `"m"^3` of air contains 30 g of water vapour at `30^circ`C.
So, amount of water vapour in 50 `"m"^3` of air at `30^circ`C = (`30 xx 50`) g = 1500 g
Also , 1 `"m"^3` of air contains 16 g of water vapour at `20^circ "C"`.
Amount of water vapour in 50 `"m"^3` of air at `20^circ`C. = `(16 xx 50)` g = 800 g
Amount of water vapour condensed = (1500 - 800) g = 700 g
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Molar volume is the volume occupied by 1 mol of any (ideal) gas at standard temperature and pressure (STP: 1 atmospheric pressure, 0 °C). Show that it is 22.4 litres
The figure shows the plot of PV/T versus Pfor 1.00×10–3 kg of oxygen gas at two different temperatures.
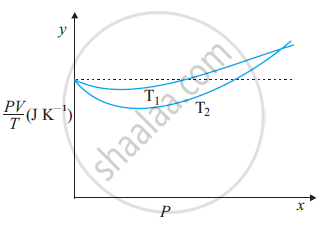
(a) What does the dotted plot signify?
(b) Which is true: T1 > T2 or T1 < T2?
(c) What is the value of PV/T where the curves meet on the y-axis?
(d) If we obtained similar plots for 1.00 ×10–3 kg of hydrogen, would we get the same value of PV/T at the point where the curves meet on the y-axis? If not, what mass of hydrogen yields the same value of PV/T (for low pressure high temperature region of the plot)? (Molecular mass of H2 = 2.02 u, of O2 = 32.0 u, R = 8.31 J mo1–1 K–1.)
An oxygen cylinder of volume 30 litres has an initial gauge pressure of 15 atm and a temperature of 27 °C. After some oxygen is withdrawn from the cylinder, the gauge pressure drops to 11 atm and its temperature drops to 17 °C. Estimate the mass of oxygen taken out of the cylinder (R = 8.31 J mol–1 K–1, molecular mass of O2 = 32 u)
Estimate the average thermal energy of a helium atom at the temperature of 10 million Kelvin (the typical core temperature in the case of a star).
At what temperature is the root mean square speed of an atom in an argon gas cylinder equal to the rms speed of a helium gas atom at – 20 °C? (atomic mass of Ar = 39.9 u, of He = 4.0 u).
Oxygen is filled in a closed metal jar of volume 1.0 × 10−3 m3 at a pressure of 1.5 × 105Pa and temperature 400 K. The jar has a small leak in it. The atmospheric pressure is 1.0 × 105 Pa and the atmospheric temperature is 300 K. Find the mass of the gas that leaks out by the time the pressure and the temperature inside the jar equalise with the surrounding.
What do you understand by gas?
Give reasons for the following:
Gas fills the vessel completely in which it is kept.
Match the following:
|
|
Column A |
Column B |
|
(a) |
cm3 |
(i) Pressure |
|
(b) |
Kelvin |
(ii) Temperature |
|
(c) |
Torr |
(iii) Volume |
|
(d) |
Boyle's law |
(iv) `"V"/"T" = ("V"_1)/("T"_1)` |
|
(a) |
Charles's law |
(v) `"PV"/"T" = ("P"_1 "V"_1)/"T"_1` |
|
|
|
(vi) PV = P1V1 |
Fill in the blanks:
If the temperature is reduced to half, ………….. would also reduce to half.
Give reason for the following:
Temperature remaining constant the product of the vol. & the press, of a given mass of dry gas is a constant.
The average energy per molecule is proportional to ______
Show that for monoatomic gas the ratio of the two specific heats is 5:3.
Show that for diatomic gas the ratio of the two specific heats is 7:5.
The equation of state for 2g of oxygen at a pressure 'P' and temperature 'T', when occupying a volume 'V' will be ______.
Estimate the average thermal energy of a helium atom at the temperature on the surface of the Sun (6000 K).
The volume V of an enclosure contains a mixture of three gases, 16 g of oxygen, 28 g of nitrogen and 44 g of carbon dioxide at absolute temperature T. Consider R as universal gas constant. The pressure of the mixture of gases is ______.
P ∝ T at constant volume is the statement of ______.
