Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Show that for monoatomic gas the ratio of the two specific heats is 5:3.
Solution
- For a monatomic gas enclosed in a container, held at a constant temperature T, and containing NA atoms, each atom has only 3 translational degrees of freedom.
- Therefore, the average energy per atom is `3/2` kBT and the total internal energy per mole is, E = `3/2` NAkBT
- Molar specific heat at constant volume
Cv = `"dE"/"dT" = 3/2"N"_"A""k"_"B" = 3/2"R"` - Using Mayer’s relation, CP = R + CV
∴ Cp = `5/2`R
∴ `"C"_"p"/"C"_"v" = 5/3`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The figure shows the plot of PV/T versus Pfor 1.00×10–3 kg of oxygen gas at two different temperatures.
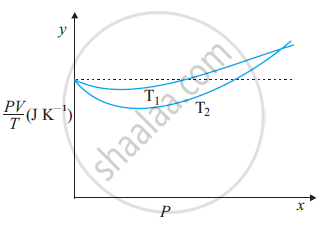
(a) What does the dotted plot signify?
(b) Which is true: T1 > T2 or T1 < T2?
(c) What is the value of PV/T where the curves meet on the y-axis?
(d) If we obtained similar plots for 1.00 ×10–3 kg of hydrogen, would we get the same value of PV/T at the point where the curves meet on the y-axis? If not, what mass of hydrogen yields the same value of PV/T (for low pressure high temperature region of the plot)? (Molecular mass of H2 = 2.02 u, of O2 = 32.0 u, R = 8.31 J mo1–1 K–1.)
Estimate the average thermal energy of a helium atom at the temperature of 10 million Kelvin (the typical core temperature in the case of a star).
At what temperature is the root mean square speed of an atom in an argon gas cylinder equal to the rms speed of a helium gas atom at – 20 °C? (atomic mass of Ar = 39.9 u, of He = 4.0 u).
Oxygen is filled in a closed metal jar of volume 1.0 × 10−3 m3 at a pressure of 1.5 × 105Pa and temperature 400 K. The jar has a small leak in it. The atmospheric pressure is 1.0 × 105 Pa and the atmospheric temperature is 300 K. Find the mass of the gas that leaks out by the time the pressure and the temperature inside the jar equalise with the surrounding.
What do you understand by gas?
During the practical session in the lab when hydrogen sulphide gas having offensive odour is prepared for some test, we can smell the gas even 50 metres away. Explain the phenomenon.
Give reasons for the following:
Gas fills the vessel completely in which it is kept.
Choose the correct answer:
The graph of PV vs P for gas is
Correct the following statement:
0°C is equal to zero Kelvin.
Name or state the following:
The standard pressure of a gas in cm. of mercury corresponding to one atmospheric pressure.
Name or state the following:
The absolute temperature value corresponding to 35°C.
Give reason for the following:
Volumes of gases are converted into s.t.p. conditions and then compared.
The average energy per molecule is proportional to ______
If the absolute temperature of a body is doubled, the power radiated will increase by a factor of ______
Show that for diatomic gas the ratio of the two specific heats is 7:5.
Gases exert pressure on the walls of the container because the gas molecules ______
The equation of state for 2g of oxygen at a pressure 'P' and temperature 'T', when occupying a volume 'V' will be ______.
Estimate the average thermal energy of a helium atom at the temperature on the surface of the Sun (6000 K).
Three vessels of equal capacity have gases at the same temperature and pressure. The first vessel contains neon (monatomic), the second contains chlorine (diatomic), and the third contains uranium hexafluoride (polyatomic).
Do the vessels contain an equal number of respective molecules?
A box of 1.00 m3 is filled with nitrogen at 1.50 atm at 300K. The box has a hole of an area 0.010 mm2. How much time is required for the pressure to reduce by 0.10 atm, if the pressure outside is 1 atm.
Cooking gas containers are kept in a lorry moving with uniform speed. The temperature of the gas molecules inside will ______.
For a wave, y = 0.0002 sin`[2pi(110"t"-x/3)+pi/3]` is travelling in a medium. The energy per unit volume being transferred by wave if density of medium is 1.5 kg/m3, is ______.
Two tanks of equal volume contain equal mass of oxygen and nitrogen at 127°C. Find the ratio of pressure in two tanks.
