Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If the absolute temperature of a body is doubled, the power radiated will increase by a factor of ______
Options
2
4
8
16
Solution
If the absolute temperature of a body is doubled, the power radiated will increase by a factor of 16.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The figure shows the plot of PV/T versus Pfor 1.00×10–3 kg of oxygen gas at two different temperatures.
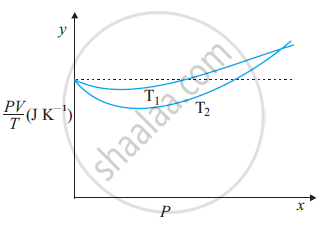
(a) What does the dotted plot signify?
(b) Which is true: T1 > T2 or T1 < T2?
(c) What is the value of PV/T where the curves meet on the y-axis?
(d) If we obtained similar plots for 1.00 ×10–3 kg of hydrogen, would we get the same value of PV/T at the point where the curves meet on the y-axis? If not, what mass of hydrogen yields the same value of PV/T (for low pressure high temperature region of the plot)? (Molecular mass of H2 = 2.02 u, of O2 = 32.0 u, R = 8.31 J mo1–1 K–1.)
Estimate the average thermal energy of a helium atom at the temperature of 10 million Kelvin (the typical core temperature in the case of a star).
Three vessels of equal capacity have gases at the same temperature and pressure. The first vessel contains neon (monatomic), the second contains chlorine (diatomic), and the third contains uranium hexafluoride (polyatomic).
Is the root mean square speed of molecules the same in the three cases? If not, in which case is vrms the largest?
50 m3 of saturated vapour is cooled down from 30°C to 20°C. Find the mass of the water condensed. The absolute humidity of saturated water vapour is 30 g m−3 at 30°C and 16 g m−3 at 20°C.
What do you understand by gas?
What is diffusion? Give an example to illustrate it.
Choose the correct answer:
The graph of PV vs P for gas is
Match the following:
|
|
Column A |
Column B |
|
(a) |
cm3 |
(i) Pressure |
|
(b) |
Kelvin |
(ii) Temperature |
|
(c) |
Torr |
(iii) Volume |
|
(d) |
Boyle's law |
(iv) `"V"/"T" = ("V"_1)/("T"_1)` |
|
(a) |
Charles's law |
(v) `"PV"/"T" = ("P"_1 "V"_1)/"T"_1` |
|
|
|
(vi) PV = P1V1 |
Fill in the blanks:
If the temperature is reduced to half, ………….. would also reduce to half.
Name or state the following:
An equation used in chemical calculations which gives a simultaneous effect of changes of temperature and pressure on the volume of a given mass of dry gas
Name or state the following:
The standard pressure of a gas in cm. of mercury corresponding to one atmospheric pressure.
Give reason for the following:
Volumes of gases are converted into s.t.p. conditions and then compared.
The average energy per molecule is proportional to ______
Show that for monoatomic gas the ratio of the two specific heats is 5:3.
Show that for diatomic gas the ratio of the two specific heats is 7:5.
Estimate the average thermal energy of a helium atom at room temperature (27 °C).
Three vessels of equal capacity have gases at the same temperature and pressure. The first vessel contains neon (monatomic), the second contains chlorine (diatomic), and the third contains uranium hexafluoride (polyatomic).
Do the vessels contain an equal number of respective molecules?
The volume V of an enclosure contains a mixture of three gases, 16 g of oxygen, 28 g of nitrogen and 44 g of carbon dioxide at absolute temperature T. Consider R as universal gas constant. The pressure of the mixture of gases is ______.
At room temperature, a diatomic gas is found to have an r.m.s. speed of 1930 ms-1. The gas is ______.
For a wave, y = 0.0002 sin`[2pi(110"t"-x/3)+pi/3]` is travelling in a medium. The energy per unit volume being transferred by wave if density of medium is 1.5 kg/m3, is ______.
P ∝ T at constant volume is the statement of ______.
Two tanks of equal volume contain equal mass of oxygen and nitrogen at 127°C. Find the ratio of pressure in two tanks.
