Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A 14.5 kg mass, fastened to the end of a steel wire of unstretched length 1.0 m, is whirled in a vertical circle with an angular velocity of 2 rev/s at the bottom of the circle. The cross-sectional area of the wire is 0.065 cm2. Calculate the elongation of the wire when the mass is at the lowest point of its path.
उत्तर १
Mass, m = 14.5 kg
Length of the steel wire, l = 1.0 m
Angular velocity, ω = 2 rev/s = 2 × 2π rad/s = 12.56 rad/s
Cross-sectional area of the wire, a = 0.065 cm2 = 0.065 × 10-4 m2
Let Δl be the elongation of the wire when the mass is at the lowest point of its path.
When the mass is placed at the position of the vertical circle, the total force on the mass is:
F = mg + mlω2
= 14.5 × 9.8 + 14.5 × 1 × (12.56)2
= 2429.53 N
Young's modulus = Stress/Strain
`Y = (F/A)/trianglel = F/A l/trianglel`
`:.trianglel = (Fl)/(AY)`
Young’s modulus for steel = 2 × 1011 Pa
`trianglel = (2429.53xx1)/(0.065xx10^(-4)xx2xx10^11)`
`=>trianglel = 1.87 xx 10^(-3) m`
Hence, the elongation of the wire is 1.87 × 10–3 m.
उत्तर २
Here, m = 14.5 kg; l = r = 1 m; v = 2 rps; A = 0.065 x 10-4 m2 Total pulling force on mass, when it is at the lowest position of the vertical circle is F = mg + mr w2 = mg + mr 4,π2 v2
`=14.5 xx 9.8 + 14.5 xx 1 xx 4 xx (22/7)^2 xx 2^2`
=142.1 + 2291.6 = 2433.9 N
`Y = F/A xx l/(trianglel)`
or `trianglel = (Fl)/(AY)= (2433.7xx1)/(0.065 xx 10^(-4)xx(2xx10^11)) = 1.87 xx 10^(-3) m = 1.87 m`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
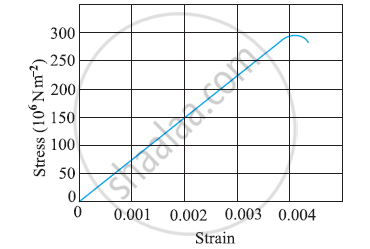
The figure shows the strain-stress curve for a given material. What are (a) Young’s modulus and (b) approximate yield strength for this material?
Four identical hollow cylindrical columns of mild steel support a big structure of mass 50,000 kg. The inner and outer radii of each column are 30 cm and 60 cm respectively. Assuming the load distribution to be uniform, calculate the compressional strain of each column.
A wire elongates by 1.0 mm when a load W is hung from it. If this wire goes over a a pulley and two weights W each are hung at the two ends, he elongation of he wire will be
A steel rod of cross-sectional area 4 cm2 and 2 m shrinks by 0.1 cm as the temperature decreases in night. If the rod is clamped at both ends during the day hours, find the tension developed in it during night hours. Young modulus of steel = 1.9 × 1011 N m−2.
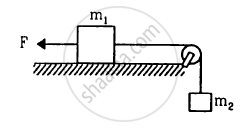
Consider the situation shown in figure. The force F is equal to the m2 g/2. If the area of cross section of the string is A and its Young modulus Y, find the strain developed in it. The string is light and there is no friction anywhere.
The temperature of a wire is doubled. The Young’s modulus of elasticity ______.
If the yield strength of steel is 2.5 × 108 Nm–2, what is the maximum weight that can be hung at the lower end of the wire?
If Y, K and η are the values of Young's modulus, bulk modulus and modulus of rigidity of any material respectively. Choose the correct relation for these parameters.
If the length of a wire is made double and the radius is halved of its respective values. Then, Young's modules of the material of the wire will ______.
The force required to stretch a wire of cross section 1 cm2 to double its length will be ______.
(Given Young's modulus of the wire = 2 × 1011 N/m2)
