Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The temperature of a wire is doubled. The Young’s modulus of elasticity ______.
पर्याय
will also double.
will become four times.
will remain same.
will decrease.
उत्तर
The temperature of a wire is doubled. The Young’s modulus of elasticity will decrease.
Explanation:
Young's modulus (Y): It is defined as the ratio of normal stress to longitudinal strain within the limit of proportionality.
`Y = "Normal stress"/"Longitudinal strain"`
= `(F/A)/((ΔL)/L)`
= `(FL)/(AΔL)`
The fractional change in length of any material is defined as `(ΔL)/L_0 = αΔT` where ΔT is the change in the temperature, L0 is the original length, α is the coefficient of linear expansion of the given material and L0 is the original length of material.
So, simply a change in length is due to change in temperature.
`ΔL = L_0αΔT`
And Young's modules
(Y) = `"Stress"/"Strain"`
= `(FL_0)/(A xx ΔL)`
= `(FL_0)/(AL_0 ΔT) ∝ 1/(ΔT)`
As Y ∝ 1/∆T
When temperature increases ∆T increases, hence Y decreases.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The stress-strain graphs for materials A and B are shown in Figure
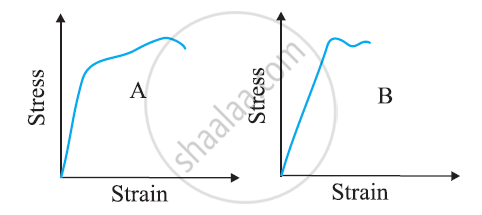
The graphs are drawn to the same scale.
(a) Which of the materials has the greater Young’s modulus?
(b) Which of the two is the stronger material?
Read the following statements below carefully and state, with reasons, if it is true or false
The Young’s modulus of rubber is greater than that of steel;
Four identical hollow cylindrical columns of mild steel support a big structure of mass 50,000 kg. The inner and outer radii of each column are 30 cm and 60 cm respectively. Assuming the load distribution to be uniform, calculate the compressional strain of each column.
The length of a metal wire is l1 when the tension in it T1 and is l2 when the tension is T2. The natural length of the wire is
A rigid bar of mass M is supported symmetrically by three wires each of length l. Those at each end are of copper and the middle one is of iron. The ratio of their diameters, if each is to have the same tension, is equal to ______.
Identical springs of steel and copper are equally stretched. On which, more work will have to be done?
A steel rod (Y = 2.0 × 1011 Nm–2; and α = 10–50 C–1) of length 1 m and area of cross-section 1 cm2 is heated from 0°C to 200°C, without being allowed to extend or bend. What is the tension produced in the rod?
In nature, the failure of structural members usually result from large torque because of twisting or bending rather than due to tensile or compressive strains. This process of structural breakdown is called buckling and in cases of tall cylindrical structures like trees, the torque is caused by its own weight bending the structure. Thus the vertical through the centre of gravity does not fall within the base. The elastic torque caused because of this bending about the central axis of the tree is given by `(Ypir^4)/(4R) . Y` is the Young’s modulus, r is the radius of the trunk and R is the radius of curvature of the bent surface along the height of the tree containing the centre of gravity (the neutral surface). Estimate the critical height of a tree for a given radius of the trunk.
A boy's catapult is made of rubber cord which is 42 cm long, with a 6 mm diameter of cross-section and negligible mass. The boy keeps a stone weighing 0.02 kg on it and stretches the cord by 20 cm by applying a constant force. When released, the stone flies off with a velocity of 20 ms-1. Neglect the change in the area of the cross-section of the cord while stretched. Young's modulus of rubber is closest to ______.
A uniform metal rod of 2 mm2 cross section is heated from 0°C to 20°C. The coefficient of linear expansion of the rod is 12 × 10-6/°C, it's Young's modulus is 1011 N/m2. The energy stored per unit volume of the rod is ______.
