Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A bar magnet is released from rest along the axis of a very long, vertical copper tube. After some time the magnet ____________ .
पर्याय
will stop in the tube
will move with almost contant speed
will move with an acceleration g
will oscillate
उत्तर
will move with almost contant speed
As the magnet is moving under gravity, the flux linked with the copper tube will change because of the motion of the magnet. This will produce eddy currents in the body of the copper tube. According to Lenz's law, these induced currents oppose the fall of the magnet. So, the magnet will experience a retarding force. This force will continuously increase with increasing velocity of the magnet till it becomes equal to the force of gravity. After this, the net force on the magnet will become zero. Hence, the magnet will attain a constant speed.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Describe a simple experiment (or activity) to show that the polarity of emf induced in a coil is always such that it tends to produce a current which opposes the change of magnetic flux that produces it.
What is the direction of induced currents in metal rings 1 and 2 when current I in the wire is increasing steadily?
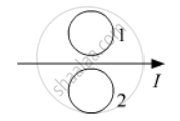
Predict the directions of induced currents in metal rings 1 and 2 lying in the same plane where current I in the wire is increasing steadily.
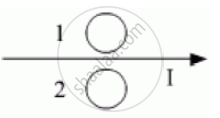
Predict the direction of induced current in metal rings 1 and 2 when current I in the wire is steadily decreasing?
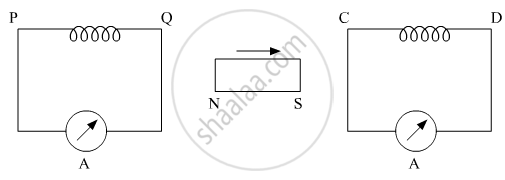
A bar magnet is moved in the direction indicated by the arrow between two coils PQ and CD. Predict the directions of induced current in each coil.
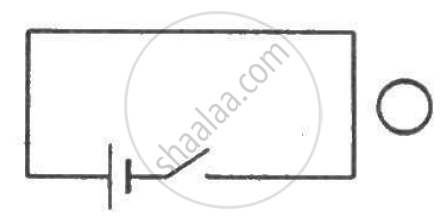
Consider the situation shown in figure. If the switch is closed and after some time it is opened again, the closed loop will show ____________ .
Two circular loops of equal radii are placed coaxially at some separation. The first is cut and a battery is inserted in between to drive a current in it. The current changes slightly because of the variation in resistance with temperature. During this period, the two loops _______________ .
A bar magnet is moved along the axis of a copper ring placed far away from the magnet. Looking from the side of the magnet, an anticlockwise current is found to be induced in the ring. Which of the following may be true?
(a) The south pole faces the ring and the magnet moves towards it.
(b) The north pole faces the ring and the magnet moves towards it.
(c) The south pole faces the ring and the magnet moves away from it.
(d) The north pole faces the ring and the magnet moves away from it.
Explain, with the help of a suitable example, how we can show that Lenz's law is a consequence of the principle of conservation of energy.
Which of the following statements is not correct?
There are two coils A and B as shown in figure. A current starts flowing in B as shown, when A is moved towards B and stops when A stops moving. The current in A is counterclockwise. B is kept stationary when A moves. We can infer that ______.

A wire in the form of a tightly wound solenoid is connected to a DC source, and carries a current. If the coil is stretched so that there are gaps between successive elements of the spiral coil, will the current increase or decrease? Explain.
A conducting wire XY of mass m and neglibile resistance slides smoothly on two parallel conducting wires as shown in figure. The closed circuit has a resistance R due to AC. AB and CD are perfect conductors. There is a ˆ. magnetic field `B = B(t)hatk`.
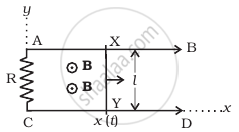
- Write down equation for the acceleration of the wire XY.
- If B is independent of time, obtain v(t) , assuming v(0) = u0.
- For (b), show that the decrease in kinetic energy of XY equals the heat lost in R.
A metallic ring of mass m and radius `l` (ring being horizontal) is falling under gravity in a region having a magnetic field. If z is the vertical direction, the z-component of magnetic field is Bz = Bo (1 + λz). If R is the resistance of the ring and if the ring falls with a velocity v, find the energy lost in the resistance. If the ring has reached a constant velocity, use the conservation of energy to determine v in terms of m, B, λ and acceleration due to gravity g.
A long solenoid ‘S’ has ‘n’ turns per meter, with diameter ‘a’. At the centre of this coil we place a smaller coil of ‘N’ turns and diameter ‘b’ (where b < a). If the current in the solenoid increases linearly, with time, what is the induced emf appearing in the smaller coil. Plot graph showing nature of variation in emf, if current varies as a function of mt2 + C.
Predict the direction of induced current in the situation described by the following figure.
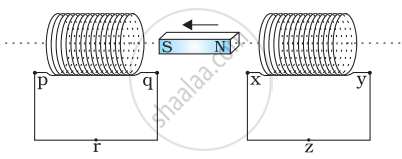
Predict the direction of induced current in the situation described by the following figure.
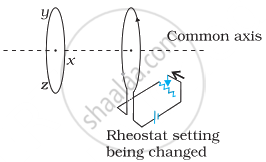
Predict the direction of induced current in the situation described by the following figure.
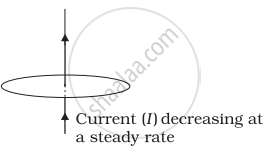
Use Lenz’s law to determine the direction of induced current in the situation described by the figure.
A circular loop being deformed into a narrow straight wire.