Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A metallic ring of mass m and radius `l` (ring being horizontal) is falling under gravity in a region having a magnetic field. If z is the vertical direction, the z-component of magnetic field is Bz = Bo (1 + λz). If R is the resistance of the ring and if the ring falls with a velocity v, find the energy lost in the resistance. If the ring has reached a constant velocity, use the conservation of energy to determine v in terms of m, B, λ and acceleration due to gravity g.
उत्तर
In this problem a relation is established between induced current, power lost and velocity acquired by freely falling ring.
The magnetic flux linked with the metallic ring of mass m and radius l ring being horizontal falling under gravity in a region having a magnetic field whose z-component of magnetic field is Bz = B0(1 + λz) is `phi = vecB_z.vecA = B_o (1 + λz).pil^2`
The angle between `vecB` and `vecA` is 0°
`ε = d/(dt) [B_o (1 + λz)]pil^2`
`IR = (B_opil^2)[0 + λ (dz)/(dt)]`
`I = (B_opiλl^2)/R (dz)/(dt) = (B_opiλl^2)/R v`
Energy lost = `I^2R = (B_o^2pi^2λ^2l^4)/R^2 v^2R`
Energy lost = `(B_o^2pi^2λ^2l^4v^2)/R`
The energy must come from decrease in P.E = `mg (dz)/(dt) = mgv`
∴ `mgv = (B_o^2pi^2λ^2v^2l^4)/R`
`v = (mgR)/(B_o^2pi^2λ^2l^4)` or `(mgR)/((pil^2λB_o)^2)`
It is the required relation.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the direction of induced currents in metal rings 1 and 2 when current I in the wire is increasing steadily?
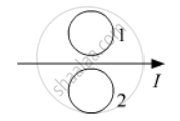
Predict the directions of induced currents in metal rings 1 and 2 lying in the same plane where current I in the wire is increasing steadily.
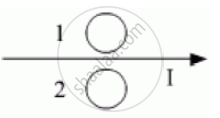
A pivoted aluminium bar falls much more slowly through a small region containing a magnetic field than a similar bar of an insulating material. Explain.
Explain, with the help of a suitable example, how we can show that Lenz's law is a consequence of the principle of conservation of energy.
Lenz’s law is a consequence of the law of conservation of ______.
For a coil having L = 2 mH, current flows at the rate of 10-3 AIS. The e.m.f induced is
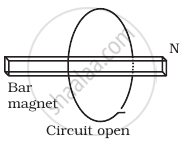
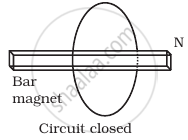
Consider a magnet surrounded by a wire with an on/off switch S (Figure). If the switch is thrown from the off position (open circuit) to the on position (closed circuit), will a current flow in the circuit? Explain.
A solenoid is connected to a battery so that a steady current flows through it. If an iron core is inserted into the solenoid, will the current increase or decrease? Explain.
A conducting wire XY of mass m and neglibile resistance slides smoothly on two parallel conducting wires as shown in figure. The closed circuit has a resistance R due to AC. AB and CD are perfect conductors. There is a ˆ. magnetic field `B = B(t)hatk`.
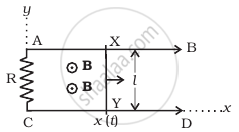
- Write down equation for the acceleration of the wire XY.
- If B is independent of time, obtain v(t) , assuming v(0) = u0.
- For (b), show that the decrease in kinetic energy of XY equals the heat lost in R.
Use Lenz’s law to determine the direction of induced current in the situation described by the figure.
A circular loop being deformed into a narrow straight wire.