Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
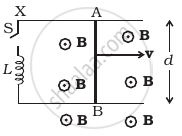
Find the current in the sliding rod AB (resistance = R) for the arrangement shown in figure. B is constant and is out of the paper. Parallel wires have no resistance. v is constant. Switch S is closed at time t = 0.
उत्तर
This is a similar problem as we discussed above. Here, a conductor of length d moves with speed v, perpendicular to magnetic field B as shown in figure.
Due to this, an motional emf is induced across two ends of rod (e = vBd).
Since, switch S is closed at time t = 0 current starts growing in the inductor by the potential difference due to motional emf.
By applying KVL in the given circuit, we have
`- L (dI)/(dt) + vBd = IR` or `L (dI)/(dt) + IR = vBd`
This is the linear differential equation.
On solving, we get
`I = (vBd)/R + Ae^((- Rt)/2)`
At t = 0, I = 0
⇒ `A = - (vBd)/R`
⇒ `I = (vBd)/R (1 - e^((- Rt)/L))`
This is the required expression of current.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A 20 cm long conducting rod is set into pure translation with a uniform velocity of 10 cm s−1 perpendicular to its length. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.10 T exists in a direction perpendicular to the plane of motion. (a) Find the average magnetic force on the free electrons of the rod. (b) For what electric field inside the rod, the electric force on a free elctron will balance the magnetic force? How is this electric field created? (c) Find the motional emf between the ends of the rod.
A conducting disc of radius r rotates with a small but constant angular velocity ω about its axis. A uniform magnetic field B exists parallel to the axis of rotation. Find the motional emf between the centre and the periphery of the disc.
A conducting square loop of side l and resistance R moves in its plane with a uniform velocity v perpendicular to one of its side. A magnetic induction B constant in time and space, pointing perpendicular and into the plane of the loop exists everywhere. The current induced in the loop is ______.
A straight conductor of length 2 m moves in a uniform magnetic field of induction 2.5 x `10^-3` T with a velocity. of 4 m/s in a direction perpendicular to its length and also perpendicular to the field. The e.m.f. induced between the ends of the conductor is ______.
A wire of length 50 cm moves with a velocity of 300 m/min, perpendicular to a magnetic field. If the e.m.f. induced in the wire is 2 V, the magnitude of the field in tesla is ______.
The emf induced across the ends of a conductor due to its motion in a magnetic field is called motional emf. It is produced due to magnetic Lorentz force acting on the free electrons of the conductor. For a circuit shown in the figure, if a conductor of length l moves with velocity v in a magnetic field B perpendicular to both its length and the direction of the magnetic field, then all the induced parameters are possible in the circuit.
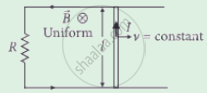
A conducting rod of length l is moving in a transverse magnetic field of strength B with velocity v. The resistance of the rod is R. The current in the rod is ______.
An e.m.f is produced in a coil, which is not connected to an external voltage source. This can be due to ______.
- the coil being in a time varying magnetic field.
- the coil moving in a time varying magnetic field.
- the coil moving in a constant magnetic field.
- the coil is stationary in external spatially varying magnetic field, which does not change with time.
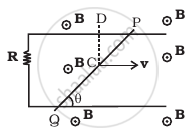
Find the current in the wire for the configuration shown in figure. Wire PQ has negligible resistance. B, the magnetic field is coming out of the paper. θ is a fixed angle made by PQ travelling smoothly over two conducting parallel wires separated by a distance d.
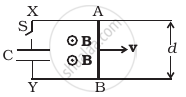
Find the current in the sliding rod AB (resistance = R) for the arrangement shown in figure. B is constant and is out of the paper. Parallel wires have no resistance. v is constant. Switch S is closed at time t = 0.
Derive an expression for the total emf induced in a conducting rotating rod.
