Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A child stands at the centre of a turntable with his two arms outstretched. The turntable is set rotating with an angular speed of 40 rev/min. How much is the angular speed of the child if he folds his hands back and thereby reduces his moment of inertia to 2/5 times the initial value? Assume that the turntable rotates without friction.
उत्तर १
Suppose, initial moment of inertia of the child is I1 Then final moment of inertia,
`I_2 = 2/3 I_l`
Also `v_1 = 40 " rev min"^(-I)`
By using the principle of conversion of angular, momentum, we get
`I_1omega_1 = I_2omega_2 or I_1(2piv_1) = I_2(2piv_2)`
or `v_2 = (I_1v_1)/I_2 = (I_1xx40)/(2/5 xx I_1) = 100 rev min^(-1)`
उत्तर २
100 rev/min
Initial angular velocity, ω1= 40 rev/min
Final angular velocity = ω2
The moment of inertia of the boy with stretched hands = I1
The moment of inertia of the boy with folded hands = I2
The two moments of inertia are related as:
`I_2 = 2/5 I_1`
Since no external force acts on the boy, the angular momentum L is a constant.
Hence, for the two situations, we can write:
`I_2omega_2 = I_1omega_1`
`omega_2=I_1/I_2 omega_1`
`= I_1/(2/5 I_1) xx 40 = 5/2 xx 40`
= 100 rev/min
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The oxygen molecule has a mass of 5.30 × 10–26 kg and a moment of inertia of 1.94×10–46 kg m2 about an axis through its centre perpendicular to the lines joining the two atoms. Suppose the mean speed of such a molecule in a gas is 500 m/s and that its kinetic energy of rotation is two thirds of its kinetic energy of translation. Find the average angular velocity of the molecule.
A cylinder of mass 10 kg and radius 15 cm is rolling perfectly on a plane of inclination 30°. The coefficient of static friction µs = 0.25.
(a) How much is the force of friction acting on the cylinder?
(b) What is the work done against friction during rolling?
(c) If the inclination θ of the plane is increased, at what value of θ does the cylinder begin to skid, and not roll perfectly?
A body having its centre of mass at the origin has three of its particles at (a,0,0), (0,a,0), (0,0,a). The moments of inertia of the body about the X and Y axes are 0⋅20 kg-m2 each. The moment of inertia about the Z-axis
A string is wrapped on a wheel of moment of inertia 0⋅20 kg-m2 and radius 10 cm and goes through a light pulley to support a block of mass 2⋅0 kg as shown in the following figure. Find the acceleration of the block.
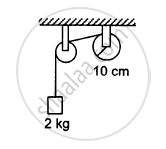
Suppose the smaller pulley of the previous problem has its radius 5⋅0 cm and moment of inertia 0⋅10 kg-m2. Find the tension in the part of the string joining the pulleys.
The descending pulley shown in the following figure has a radius 20 cm and moment of inertia 0⋅20 kg-m2. The fixed pulley is light and the horizontal plane frictionless. Find the acceleration of the block if its mass is 1⋅0 kg.
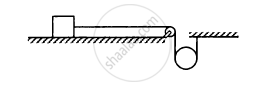
Solve the previous problem if the friction coefficient between the 2⋅0 kg block and the plane below it is 0⋅5 and the plane below the 4⋅0 kg block is frictionless.
A kid of mass M stands at the edge of a platform of radius R which can be freely rotated about its axis. The moment of inertia of the platform is I. The system is at rest when a friend throws a ball of mass m and the kid catches it. If the velocity of the ball is \[\nu\] horizontally along the tangent to the edge of the platform when it was caught by the kid, find the angular speed of the platform after the event.
Four bodies of masses 2 kg, 3 kg, 4 kg and 5 kg are placed at points A, B, C, and D respectively of a square ABCD of side 1 metre. The radius of gyration of the system about an axis passing through A and perpendicular to plane is
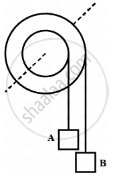
The figure shows a small wheel fixed coaxially on a bigger one of double the radius. The system rotates about the common axis. The strings supporting A and B do not slip on the wheels. If x and y be the distances travelled by A and B in the same time interval, then ______.