Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A current loop of arbitrary shape lies in a uniform magnetic field B. Show that the net magnetic force acting on the loop is zero.
उत्तर
Given:
Uniform magnetic field existing in the region of the arbitrary loop = B
Let the electric current flowing through the loop be i.
Length of each side of the loop is l.
Assume that the direction of the current is clockwise.
Direction of the magnetic field is going into the plane of the loop.
Magnetic force is given by
`vecF = i veclxxvecB`
`vecF = ilBsintheta`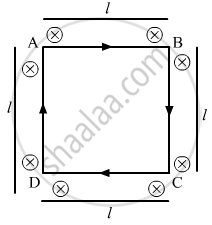
Here, θ = 90˚
Direction of force can be found using Fleming's lef- hand rule.
Force F1 acting on AB = ilB upwards
Force F2 acting on DC = ilB downwards
So, F1 and F2 cancel each other.
Force F3 acting on AD = ilB outwards (Pointing towards the left from AB)
Force F4 acting on BC = ilB outwards (Pointing towards the right from BC)
So, F3 and F4 cancel each other.
Therefore, the net force acting on the arbitrary loop is 0.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two identical circular loops, P and Q, each of radius r and carrying equal currents are
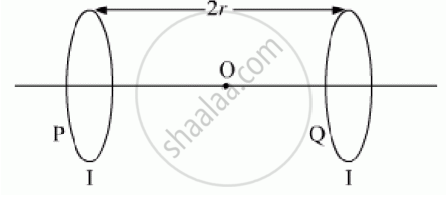
kept in the parallel planes having a common axis passing through O. The direction of current in P is clockwise and in Q is anti-clockwise as seen from O which is equidistant from the loops P and Q. Find the magnitude of the net magnetic field at O.
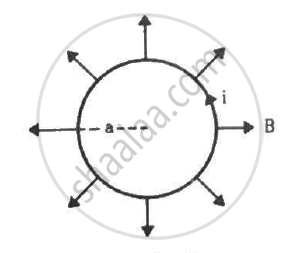
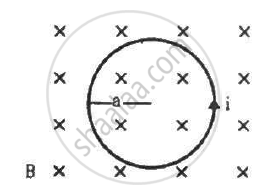
A circular loop of radius a, carrying a current i, is placed in a two-dimensional magnetic field. The centre of the loop coincides with the centre of the field (figure). The strength of the magnetic field at the periphery of the loop is B. Find the magnetic force on the wire.
A rectangular wire-loop of width a is suspended from the insulated pan of a spring balance, as shown in the figure. A current i exists in the anti-clockwise direction in the loop. A magnetic field B exists in the lower region. Find the change in the tension of the spring if the current in the loop is reversed.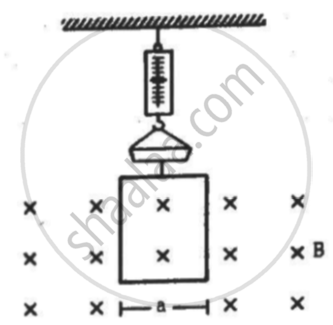
The figure shows a circular wire loop of radius a and carrying a current i, which is placed in a perpendicular magnetic field B. (a) Consider a small part dl of the wire. Find the force on this part of the wire exerted by the magnetic field. (b) Find the force of compression in the wire.
A moving coil galvanometer has been fitted with a rectangular coil having 50 turns and dimensions 5 cm × 3 cm. The radial magnetic field in which the coil is suspended is of 0.05 Wb/m2. The torsional constant of the spring is 1.5 × 10−9 Nm/degree. Obtain the current required to be passed through the galvanometer so as to produce a deflection of 30°.
A 100 turn rectangular coil measuring 0.02 m x 0.06 m of an ammeter is in a magnetic field of induction 0.4 tesla. The torsional constant of the suspension fibre is 5 x 10-7 newton x metre/degree. The maximum reading of the ammeter corresponds to a deflection of the coil through 30°. If the magnetic field is radial, then the maximum current that can be measured with this ammeter is ____________.
The `(tau - theta)` graph for a coil is
A small cylindrical soft iron piece is kept in a galvanometer so that
A rectangular coil has 200 turns each of area 50 cm2 . It is capable of rotation about an axis joining the mid points of two opposite sides. When a current of 10 A is passed through it while its plane is at right angles to a uniform magnetic field, it experiences a torque of 5 Nm. The magnetic field will be ____________.
The magnetic field developed due to current carrying coil at its centre is 'B'. If the new coil of two turns is prepared from the above coil and same current is passed, then the magnetic field at the centre of the new coil will be ____________.
A circular coil of 20 turns and radius 10 cm is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 0.10 T normal to the plane of the coil. If the current in the coil is 5.0 A, what is the
(a) total torque on the coil,
(b) total force on the coil,
(c) average force on each electron in the coil due to the magnetic field?
(The coil is made of copper wire of cross-sectional area 10–5 m2, and the free electron density in copper is given to be about 1029 m–3.)
When the plane of the coil is parallel to the field, torque will be ______
A uniform conducting wire of length 12a and resistance R is wound up as a current-carrying coil in the shape of (i) an equilateral triangle of side a; (ii) a square of sides a and, (iii) a regular hexagon of sides a. The coil is connected to a voltage source V0. Find the magnetic moment of the coils in each case.
The initial pressure and volume of a gas enclosed in a cylinder are 2 × 105 N/m2 and 6 × 10-3 m3 respectively. If the work done in compressing the gas at constant pressure is 150 J. find the final volume of the gas.
A thin flexible wire of length L is connected to two adjacent fixed points and carries a current I in the clockwise direction, as shown in the figure. When the system is put in a uniform magnetic field of strength B going into the plane of the paper, the wire takes the shape of a circle. The tension in the wire is ______.
A rectangular coil of 10 turns, each of area 0.05 m2, is suspended freely in a radial magnetic field of 0.01 T. If the torsional constant of the suspension fibre is 5 × 10−9 N·m per degree, find the angle through which the coil rotates when a current of 30 μA is passed through it.
Write the formula for torque acting on rotating current carrying coil in terms of magnetic dipole moment, in vector form.
