Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A man has to go 50 m due north, 40 m due east and 20 m due south to reach a field. (a) What distance he has to walk to reach the field? (b) What is his displacement from his house to the field?
उत्तर
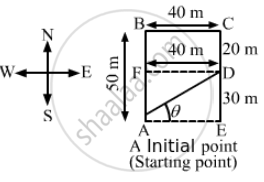
(a) Distance travelled by the man = AB + BC + CD = 50 + 40 + 20 = 110 m
(b) AF = AB − BF = 50 − 20 = 30 m
Displacement = Final position − Initial position = AD
\[\therefore AD = \sqrt{{AF}^2 + {DF}^2} = \sqrt{{30}^2 + {40}^2}\]
\[ = 50 \text{ m } \]
In ∆AED,
\[\tan \theta = \frac{DE}{AE} = \frac{30}{40}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \theta = \tan^{- 1} \left( \frac{3}{4} \right)\]
Displacement from the house to the field = 50 m in the direction \[\tan^{- 1} \left( \frac{3}{4} \right)\] north to east.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The position-time (x-t) graphs for two children A and B returning from their school O to their homes P and Q respectively, are shown in the figure. Choose the correct entries in the brackets below;
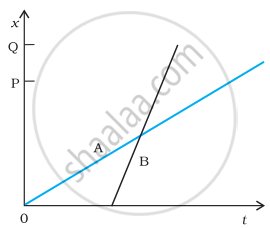
- (A/B) lives closer to the school than (B/A)
- (A/B) starts from the school earlier than (B/A)
- (A/B) walks faster than (B/A)
- A and B reach home at the (same/different) time
- (A/B) overtakes (B/A) on the road (once/twice).
A police van moving on a highway with a speed of 30 km h–1 fires a bullet at a thief’s car speeding away in the same direction with a speed of 192 km h–1. If the muzzle speed of the bullet is 150 m s–1, with what speed does the bullet hit the thief’s car? (Note: Obtain that speed which is relevant for damaging the thief’s car).
Two projectiles A and B are projected with angle of projection 15° for the projectile A and 45° for the projectile B. If RA and RB be the horizontal range for the two projectiles, then
A particle moves along the X-axis as x = u (t − 2 s) + a (t − 2 s)2.
(a) the initial velocity of the particle is u
(b) the acceleration of the particle is a
(c) the acceleration of the particle is 2a
(d) at t = 2 s particle is at the origin.
A particle starts from the origin, goes along the X-axis to the point (20 m, 0) and then return along the same line to the point (−20 m, 0). Find the distance and displacement of the particle during the trip.
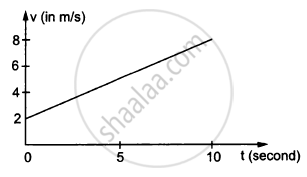
In the following figure Shows the graph of velocity versus time for a particle going along the X-axis. Find the acceleration
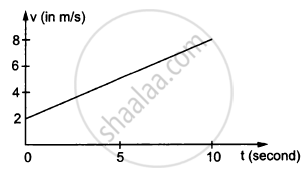
In the following figure Shows the graph of velocity versus time for a particle going along the X-axis. Find the distance travelled in 0 to 10s
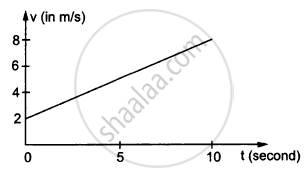
In the following figure Shows the graph of velocity versus time for a particle going along the X-axis. Find the displacement in 0 to 10 s.
A ball is dropped and its displacement vs time graph is as shown figure (displacement x is from ground and all quantities are +ve upwards).

- Plot qualitatively velocity vs time graph.
- Plot qualitatively acceleration vs time graph.
A man runs across the roof-top of a tall building and jumps horizontally with the hope of landing on the roof of the next building which is of a lower height than the first. If his speed is 9 m/s, the (horizontal) distance between the two buildings is 10 m and the height difference is 9 m, will he be able to land on the next building? (take g = 10 m/s2)
The velocity-displacement graph of a particle is shown in figure.
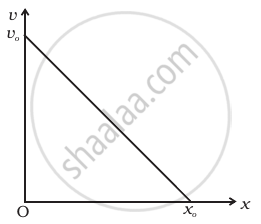
- Write the relation between v and x.
- Obtain the relation between acceleration and displacement and plot it.
Ship A is sailing towards the northeast with velocity `vecv = 30hati + 50hatj` km/hr where `hati` points east and `hatj`, north. Ship B is at a distance of 80 km east and 150 km north of Ship A and is sailing west at 10 km/hr. A will be at the minimum distance from B in ______.
A car covers the first half of the distance between two places at 40 km/h and other half at 60 km/h. The average speed of the car is ______.
