Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A metal sphere of radius 1 mm and mass 50 mg falls vertically in glycerine. Find (a) the viscous force exerted by the glycerine on the sphere when the speed of the sphere is 1 cm s−1, (b) the hydrostatic force exerted by the glycerine on the sphere and (c) the terminal velocity with which the sphere will move down without acceleration. Density of glycerine = 1260 kg m−3 and its coefficient of viscosity at room temperature = 8.0 poise.
उत्तर
Given:
Radius of metallic sphere r = 1 mm = 10−3 m
Speed of the sphere v = 10−2 m/s
Coefficient of viscosity η = 8 poise = 0.8 decapoise
Mass m = 50 mg = 50 × 10−3 kg
Density of glycerin σ = 1260 kg/m3
(a) Viscous force exerted by glycerine on the sphere F = 6πηrv
⇒ F= 6 × (3.14) × (0.8) × 10−3 × (10−2)
= 1.50 × 10−4 N
(b) Let V be the volume of the sphere.
Hydrostatic force exerted by glycerin on the sphere
\[F' = V\sigma g\]
\[\Rightarrow F' = \frac{4}{3}\pi r^2 \sigma g\]
\[= \left( \frac{4}{3} \right) \times \left( 3 . 14 \right) \times \left( {10}^{- 6} \right) \times 1260 \times 10\]
\[ = 5 . 275 \times {10}^{- 5} \text{N}\]
(c) Let the terminal velocity of the sphere be v'.
The forces acting on the drops are
(i) The weight mg acting downwards
(ii) The force of buoyance, i.e., \[\frac{4}{3}\pi r^3 \sigma g\] acting upwards
(iii) The force of viscosity, i.e., 6πηrv' acting upwards
From the free body diagram:
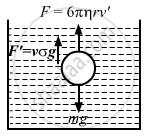
\[6\pi\eta r v' + \frac{4}{3}\pi r^3 \sigma g = \text{ mg}\]
\[ \Rightarrow v = \frac{\text{ mg }- \frac{4}{3}\pi r^2 \sigma g}{6\pi\eta r}\]
\[ = \frac{50 \times {10}^{- 3} - \frac{4}{3} \times 3 . 14 \times {10}^{- 6} \times 1260 \times 10}{6 \times 3 . 14 \times 0 . 8 \times {10}^{- 3}}\]
\[ = \frac{500 - \frac{4}{3} \times 3 . 14 \times {10}^{- 3} \times 1260 \times 10}{6 \times 3 . 14 \times 0 . 8}\]
\[ = 2 . 3 \text{ cm/s }\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Fill in the blanks using the word(s) from the list appended with each statement
For solids with elastic modulus of rigidity, the shearing force is proportional to . . . , while for fluids it is proportional to . .. (shear strain / rate of shear strain)
Explain why The size of the needle of a syringe controls flow rate better than the thumb pressure exerted by a doctor while administering an injection
The force of viscosity is
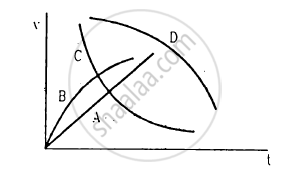
A spherical ball is dropped in a long column of a viscous liquid. The speed of the ball as a function of time may be best represented by the graph
Water flows at a speed of 6 cm s−1 through a tube of radius 1 cm. Coefficient of viscosity of water at room temperature is 0.01 poise. Calculate the Reynolds number. Is it a steady flow?
Write down the expression for Stoke’s force and explain the symbols involved in it.
Derive the expression for the terminal velocity of a sphere moving in a high viscous fluid using stokes force.
Why two holes are made to empty an oil tin?
The tangential force or viscous drag on any layer of the liquid is directly proportional to the velocity gradient `"dv"/"dx"`. Then the direction of dx velocity gradient is ____________.
In motors, more viscous oil is used in summer than in winter due to ____________.
The velocity of water in river is 8 km/hr of the upper surface. The river is 12 m deep. If the coefficient of viscosity of water is 10-2 poise then the shearing stress between horizontal layers of water is ______.
Analogy
Viscous force: ______:: Buoyant force: ______.
The velocity of a small ball of mass 0.3 g and density 8 g/cc when dropped in a container filled with glycerine becomes constant after some time. If the density of glycerine is 1.3 g/cc, then the value of viscous force acting on the ball will be x × 10-4 N, and the value of x is ______.
[use g = 10 m/s2]
An air bubble of negligible weight having radius r rises steadily through a solution of density σ at speed v. The coefficient of viscosity of the solution is given by ______.
State the formula and S.I. units of coefficient of viscosity.
An incompressible liquid is flowing through a uniform cross-sectional tube with a velocity 12 cm/ s. If the thickness of liquid layer is 0.8 cm, what is the velocity gradient of that flow of liquid?
A force of 0.01 N is required to move a flat glass plate of area of 10 cm2 with a uniform velocity of 1 cm/ s over the surface of a liquid 2 mm thick. If the coefficient of viscosity of the liquid is 20 poise, the velocity gradient in the liquid layer is ______.
A water pipe with diameter of 5.0 cm is connected to another pipe of diameter 2.5 cm. How would the speeds of the water flow compare?
