Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Estimate the speed of vertically falling raindrops from the following data. Radius of the drops = 0.02 cm, viscosity of air = 1.8 × 10−4 poise, g= 9.9 × 10 ms−2 and density of water = 1000 kg m−3.
उत्तर
Given:
Radius of the drops r = 0.02 cm = 2 × 10−4 m
Viscosity of air η = 1.8 × 10−4 poise = 1.8 × 10−5 decapoise
Acceleration due to gravity g = 9.9 m/s2
Density of water ρ = 1000 kg/m3
Let v be the terminal velocity of a drop.
The forces acting on the drops are
(i) The weight mg acting downwards
(ii) The force of buoyance, i.e., \[\left( \frac{4}{3} \right) \pi r^3 \rho g\] acting upwards
(iii) The force of viscosity, i.e., 6πηrv acting upwards
Because the density of air is very small, the force of buoyance can be neglected.
From the free body diagram:
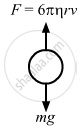
\[6\pi\eta \text{ rv = mg }\]
\[6\pi\eta rv = \frac{4}{3}\pi r^3 \rho g\]
\[v = 2 r^2 \frac{\rho g}{9\eta}\]
\[= 2 \times \left( 0 . 02 \times {10}^{- 2} \right)^2 \times 1000 \times \frac{\left( 9 . 9 \right)}{9} \times \left( 1 . 8 \times {10}^{- 5} \right)\]
\[ = 5 \text{ m/s }.\]
Hence, the required vertical speed of the falling raindrops is 5 m/s.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Fill in the blanks using the word(s) from the list appended with each statement
Viscosity of gases. .. with temperature, whereas viscosity of liquids . . . with temperature (increases / decreases)
Fill in the blanks using the word(s) from the list appended with each statement
For solids with elastic modulus of rigidity, the shearing force is proportional to . . . , while for fluids it is proportional to . .. (shear strain / rate of shear strain)
In Millikan’s oil drop experiment, what is the terminal speed of an uncharged drop of radius 2.0 × 10–5 m and density 1.2 × 103 kg m–3? Take the viscosity of air at the temperature of the experiment to be 1.8 × 10–5 Pa s. How much is the viscous force on the drop at that speed? Neglect buoyancy of the drop due to air.
The viscous force acting between two layers of a liquid is given by \[\frac{F}{A} = - \eta\frac{dv}{dz}\]. This F/A may be called
Water flows at a speed of 6 cm s−1 through a tube of radius 1 cm. Coefficient of viscosity of water at room temperature is 0.01 poise. Calculate the Reynolds number. Is it a steady flow?
With an increase in temperature, the viscosity of liquid and gas, respectively will __________.
In a horizontal pipe of non-uniform cross-section, water flows with a velocity of 1 ms−1 at a point where the diameter of the pipe is 20 cm. The velocity of water (1.5 ms−1) at a point where the diameter of the pipe is (in cm)
Define terminal velocity.
Derive the expression for the terminal velocity of a sphere moving in a high viscous fluid using stokes force.
Derive Poiseuille’s formula for the volume of a liquid flowing per second through a pipe under streamlined flow.
Why two holes are made to empty an oil tin?
From amongst the following curves, which one shows the variation of the velocity v with time t for a small-sized spherical body falling vertically in a long column of a viscous liquid.
Analogy
Viscous force: ______:: Buoyant force: ______.
Clouds float in the air due to ______.
A spherical solid ball of volume V is made of a material of density ρ1. It is falling through a liquid of density ρ2 (ρ2 < ρ1). Assume that the liquid applies a viscous force on the ball that is proportional to the square of its speed v, i.e., `"F"_"viscous"`= -kv2 (k > 0). The terminal speed of the ball is ______.
The coefficient of apparent expansion of mercury in a glass vessel is 153 × 10-6/°C and in a steel vessel is 144 × 10-6/°C. If α for steel is 12 × 10-6/°C, then that of glass is ______.
A liquid of density ρ and coefficient of viscosity η flows with velocity v through a tube of diameter D. A quantity `"R" = (rho"vD")/η`, determines whether the flow will be streamlined or turbulent. R has the dimension of ______.
Define velocity gradient.
An incompressible liquid is flowing through a uniform cross-sectional tube with a velocity 12 cm/ s. If the thickness of liquid layer is 0.8 cm, what is the velocity gradient of that flow of liquid?
