Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Derive the expression for the terminal velocity of a sphere moving in a high viscous fluid using stokes force.
उत्तर
Expression for terminal velocity: Consider a sphere of radius r which falls freely through a highly viscous liquid of coefficient of viscosity η. Let the density of the material of the sphere be ρ and the density of the fluid be σ.
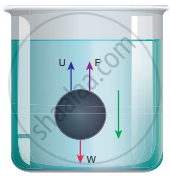
Forces acting on the sphere when it falls in a viscous liquid
Gravitational force acting on the sphere,
FG = mg = `4/3π"r"^3ρ"g"` (downward force)
Upthrust, U = `4/3π"r"^3σ"g"` (upward force)
Viscous force, F = 6πηrvt
At terminal velocity vt,
Downward force = upward force
FG = U + F
FG − U = F ⇒ `4/3π"r"^3ρ"g" - 4/3π"r"^3σ"g"` = 6πηrvt
vt = `2/9 xx ("r"^2(ρ - σ))/η` g ⇒ `"v"_"t" ∝ "r"^2`
Here, it should be noted that the terminal speed of the sphere is directly proportional to the square of its radius. If a is greater than ρ, then the term (ρ – σ) becomes negative leading to a negative terminal velocity.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The force of viscosity is
Estimate the speed of vertically falling raindrops from the following data. Radius of the drops = 0.02 cm, viscosity of air = 1.8 × 10−4 poise, g= 9.9 × 10 ms−2 and density of water = 1000 kg m−3.
A small sphere of radius 2 cm falls from rest in a viscous liquid. Heat is produced due to viscous force. The rate of production of heat when the sphere attains its terminal velocity is proportional to
In a horizontal pipe of non-uniform cross-section, water flows with a velocity of 1 ms−1 at a point where the diameter of the pipe is 20 cm. The velocity of water (1.5 ms−1) at a point where the diameter of the pipe is (in cm)
Define terminal velocity.
Why two holes are made to empty an oil tin?
A small metal sphere of mass M and density d1, when dropped in a jar filled with liquid moves with terminal velocity after sometime. The viscous force acting on the sphere is (d2 = density of liquid and g = gravitational acceleration)
In motors, more viscous oil is used in summer than in winter due to ____________.
Is viscosity a vector?
The velocity of a small ball of mass 0.3 g and density 8 g/cc when dropped in a container filled with glycerine becomes constant after some time. If the density of glycerine is 1.3 g/cc, then the value of viscous force acting on the ball will be x × 10-4 N, and the value of x is ______.
[use g = 10 m/s2]
