Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A metallic loop is placed in a nonuniform magnetic field. Will an emf be induced in the loop?
उत्तर
According to Faraday's Law, an emf is induced in a loop when the magnetic flux through the loop changes. If the magnetic field is nonuniform, the flux through the loop changes as the position of the loop changes relative to the magnetic field or if the strength of the magnetic field varies over time. This change in flux induces an emf in the loop. Therefore, in a nonuniform magnetic field, there will be a change in magnetic flux through the loop, leading to the induction of an emf.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Ram is a student of class X in a village school. His uncle gifted him a bicycle with a dynamo fitted in it. He was very excited to get it. While cycling during night, he could light the bulb and see the objects on the road. He, however, did not know how this device works. he asked this question to his teacher. The teacher considered it an opportunity to explain the working to the whole class.
Answer the following questions:
(a) State the principle and working of a dynamo.
(b) Write two values each displayed by Ram and his school teacher.
A pair of adjacent coils has a mutual inductance of 1.5 H. If the current in one coil changes from 0 to 20 A in 0.5 s, what is the change of flux linkage with the other coil?
A rectangular coil having 60 turns and area of 0.4m2 is held at right angles to a uniform magnetic field of flux density 5 × 10-5T. Calculate the magnetic flux passing through it.
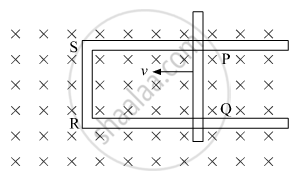
Figure shows a rectangular loop conducting PQRS in which the arm PQ is free to move. A uniform magnetic field acts in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the loop. Arm PQ is moved with a velocity v towards the arm Rs. Assuming that the arms QR, RS and SP have negligible resistances and the moving arm PQ has the resistance r, obtain the expression for (i) the current in the loop (ii) the force and (iii) the power required to move the arm PQ.
An inductor is connected to a battery through a switch. Explain why the emf induced in the inductor is much larger when the switch is opened as compared to the emf induced when the switch is closed.
Answer the following question.
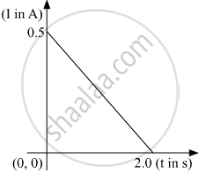
When a conducting loop of resistance 10 Ω and area 10 cm2 is removed from an external magnetic field acting normally, the variation of induced current-I in the loop with time t is as shown in the figure.
Find the
(a) total charge passed through the loop.
(b) change in magnetic flux through the loop
(c) magnitude of the field applied
Whenever the magnetic flux linked with an electric circuit changes, an emf is induced in the circuit. This is called ______.
The magnetic flux linked with a coil of N turns of area of cross-section A held with its plane parallel to the field B is ______.
Two inductors of inductance L each are connected in series with the opposite? magnetic fluxes. The resultant inductance is ______.
The dimensional formula of magnetic flux is ______.
A square of side L meters lies in the x-y plane in a region, where the magnetic field is given by `B = Bo(2hati + 3hatj + 4hatk)`T, where B0 is constant. The magnitude of flux passing through the square is ______.
A loop, made of straight edges has six corners at A(0, 0, 0), B(L, O, 0) C(L, L, 0), D(0, L, 0) E(0, L, L) and F(0, 0, L). A magnetic field `B = B_o(hati + hatk)`T is present in the region. The flux passing through the loop ABCDEFA (in that order) is ______.
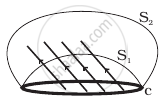
Consider a closed loop C in a magnetic field (Figure). The flux passing through the loop is defined by choosing a surface whose edge coincides with the loop and using the formula φ = B1.dA1 + B2.dA2 +... Now if we chose two different surfaces S1 and S2 having C as their edge, would we get the same answer for flux. Jusity your answer.
A circular coil of 1000 turns each with area 1 m2 is rotated about its vertical diameter at the rate of one revolution per second in a uniform horizontal magnetic field of 0.07T. The maximum voltage generation will be ______ V.
A circular coil has radius ‘r', number of turns ‘N’ and carries a current ‘I’. Magnetic flux density ‘B’ at its centre is ______.
The Figure below shows an infinitely long metallic wire YY' which is carrying a current I'.
P is a point at a perpendicular distance r from it.
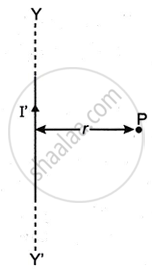
- What is the direction of magnetic flux density B of the magnetic field at the point P?
- What is the magnitude of magnetic flux density B of the magnetic field at the point P?
- Another metallic wire MN having length l and carrying a current I is now kept at point P. If the two wires are in vacuum and parallel to each other, how much force acts on the wire MN due to the current I' flowing in the wire YY'?
