Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A particle of charge ‘q’ and mass ‘m’ is moving with velocity .`vecV` It is subjected to a uniform magnetic field `vecB` directed perpendicular to its velocity. Show that it describes a circular path. Write the expression for its radius.
उत्तर
A charge ‘q’ projected perpendicular to the uniform magnetic field ‘B’ with velocity ‘v’. The perpendicular force F = qv × B acts like a centripetal force perpendicular to the magnetic field. Then the path followed by charge is circular as shown in the figure below.
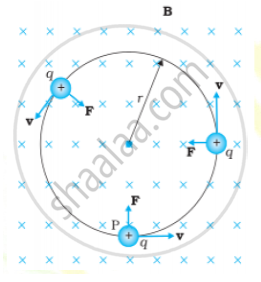
The Lorentz magnetic force acts as centripetal force thus,
`qvB =(mv^2)/r`
`r =(mv)/(qB)`
Here, r = radius of the circular path followed by charge projected perpendicular to the uniform magnetic field.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define one tesla using the expression for the magnetic force acting on a particle of charge q moving with velocity \[\vec{v}\] in a magnetic field \[\vec{B}\] .
Two wires carrying equal currents i each, are placed perpendicular to each other, just avoiding a contact. If one wire is held fixed and the other is free to move under magnetic forces, what kind of motion will result?
A charged particle is in motion having initial velocity `vecv` when it enters into a region of uniform magnetic field perpendicular to `vecv`. Because of the magnetic force the kinetic energy of the particle will ______.
The force between two parallel current-carrying conductors is F. If the current in each conductor is doubled, then the force between them becomes ______
Explain "Magnetic force never does any work on moving charges".
A proton enters into a magnetic field of induction 1.732 T, with a velocity of 107 m/s at an angle 60° to the field. The force acting on the proton is e = 1.6 × 10-19 C, sin 60° = cos 30° = `sqrt3/2`
- If v is parallel to B, then path of particle is spiral.
- If v is perpendicular to B, then path of particle is a circle.
- If v has a component along B, then path of particle is helical.
- If v is along B, then path of particle is a circle.
What is the magnetic induction of the field at the point O in a current I carrying wire that has the shape shown in the figure? The radius of the curved part of the wire is R, the linear parts are assumed to be very long.

Two charged particles traverse identical helical paths in a completely opposite sense in a uniform magnetic field B = B0k̂.
A charge particle moves along circular path in a uniform magnetic field in a cyclotron. The kinetic energy of the charge particle increases to 4 times its initial value. What will be the ratio of new radius to the original radius of circular path of the charge particle:
