Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A raindrop of mass 1.00 g falling from a height of 1 km hits the ground with a speed of 50 ms–1. Calculate
- the loss of P.E. of the drop.
- the gain in K.E. of the drop.
- Is the gain in K.E. equal to a loss of P.E.? If not why.
Take g = 10 ms–2
उत्तर
Given, the mass of the raindrop (m) = 100 g
= 1 × 10–2 kg
Height of falling (h) = 1 km = 103 m
g = 10 m/s2
Speed of the raindrop (v) = 50 m/s
a. Loss of PE of the drop (v) = 50 m/s
= 1 × 10–3 × 10 × 103
= 10 J
b. Gain in KE of the drop = `1/2 mv^2`
= `1/2 xx 1 xx 10^-3 xx (50)^2`
= `1/2 xx 10^-3 xx 2500`
= 1.250 J
c. No, the gain in KE is not equal to the loss in its PE, because a part of PE is utilised in doing work against the viscous drag of air.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An unruly demonstrator lifts a stone of mass 200 g from the ground and throws it at his opponent. At the time of projection, the stone is 150 cm above the ground and has a speed of 3 m/s. Calculate the work done by the demonstrator during the process. If it takes one second for the demonstrator to lift the stone and throw it, what horsepower does he use?
In a factory, 2000 kg of metal needs to be lifted by an engine through a distance of 12 m in 1 minute. Find the minimum horsepower of the engine to be used.
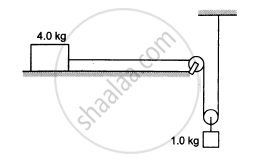
Consider the situation shown in the following figure. The system is released from rest and the block of mass 1 kg is found to have a speed 0⋅3 m/s after it has descended a distance of 1 m. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the table.
A small block of mass 200 g is kept at the top of a frictionless incline which is 10 m long and 3⋅2 m high. How much work was required (a) to lift the block from the ground and put it an the top, (b) to slide the block up the incline? What will be the speed of the block when it reaches the ground if (c) it falls off the incline and drops vertically to the ground (d) it slides down the incline? Take g = 10 m/s2.
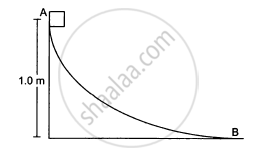
A block weighing 10 N travels down a smooth curved track AB joined to a rough horizontal surface (In the following figure). The rough surface has a friction coefficient of 0⋅20 with the block. If the block starts slipping on the track from a point 1⋅0 m above the horizontal surface, how far will it move on the rough surface?
A simple pendulum consists of a 50 cm long string connected to a 100 g ball. The ball is pulled aside so that the string makes an angle of 37° with the vertical and is then released. Find the tension in the string when the bob is at its lowest position.
A particle slides on the surface of a fixed smooth sphere starting from the topmost point. Find the angle rotated by the radius through the particle, when it leaves contact with the sphere.
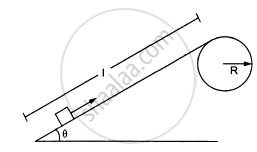
Figure ( following ) shows a smooth track which consists of a straight inclined part of length l joining smoothly with the circular part. A particle of mass m is projected up the incline from its bottom. Assuming that the projection-speed is \[\nu_0\] and that the block does not lose contact with the track before reaching its top, find the force acting on it when it reaches the top.
A chain of length l and mass m lies on the surface of a smooth sphere of radius R > l with one end tied to the top of the sphere. Find the tangential acceleration \[\frac{d\nu}{dt}\] of the chain when the chain starts sliding down.
An electron and a proton are moving under the influence of mutual forces. In calculating the change in the kinetic energy of the system during motion, one ignores the magnetic force of one on another. This is because ______.
