Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Figure ( following ) shows a smooth track which consists of a straight inclined part of length l joining smoothly with the circular part. A particle of mass m is projected up the incline from its bottom. Assuming that the projection-speed is \[\nu_0\] and that the block does not lose contact with the track before reaching its top, find the force acting on it when it reaches the top.
उत्तर
(b) When the block is projected at a speed:
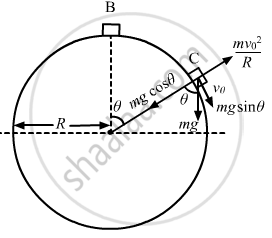
Let the velocity at C be \[\nu_0\] .
Applying energy principle,
\[\left( \frac{1}{2} \right) \text{m}\nu_0^2 - \left( \frac{1}{2} \right) \text{m}\left( 2 \nu_0 \right)^2 \]
\[ = - \text{mg} \left[ \text{ l } \sin \theta + R \left( 1 - \cos \theta \right) \right]\]
\[ \Rightarrow V^2 = 4 \nu_0^2 - 2g \left[ \text{ l } \sin g \theta + R \left( 1 - \cos \theta \right) \right]\]
\[ = 4 . 2 g \left[ \text{ l } \sin \theta + R \left( 1 - \cos \theta \right) \right] - \]
\[2g \left[ \text{ l } \sin \theta + R \left( 1 - \cos \theta \right) \right]\]
So, force acting on the body,
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Consider the situation of the previous question from a frame moving with a speed v0 parallel to the initial velocity of the block. (a) What are the initial and final kinetic energies? (b) What is the work done by the kinetic friction?
The US athlete Florence Griffith-Joyner won the 100 m sprint gold medal at Seoul Olympics in 1988, setting a new Olympic record of 10⋅54 s. Assume that she achieved her maximum speed in a very short time and then ran the race with that speed till she crossed the line. Take her mass to be 50 kg. Calculate the kinetic energy of Griffith-Joyner at her full speed.
The US athlete Florence Griffith-Joyner won the 100 m sprint gold medal at Seoul Olympics in 1988, setting a new Olympic record of 10⋅54 s. Assume that she achieved her maximum speed in a very short time and then ran the race with that speed till she crossed the line. Take her mass to be 50 kg. Assuming that the track, wind etc. offered an average resistance of one-tenth of her weight, calculate the work done by the resistance during the run.
A scooter company gives the following specifications about its product:
Weight of the scooter − 95 kg
Maximum speed − 60 km/h
Maximum engine power − 3⋅5 hp
Pick up time to get the maximum speed − 5 s
Check the validity of these specifications.
A block of mass 30 kg is being brought down by a chain. If the block acquires a speed of 40 cm/s in dropping down 2 m, find the work done by the chain during the process.
A simple pendulum consists of a 50 cm long string connected to a 100 g ball. The ball is pulled aside so that the string makes an angle of 37° with the vertical and is then released. Find the tension in the string when the bob is at its lowest position.
Following figure following shows a smooth track, a part of which is a circle of radius R. A block of mass m is pushed against a spring of spring constant k fixed at the left end and is then released. Find the initial compression of the spring so that the block presses the track with a force mg when it reaches the point P, where the radius of the track is horizontal.

A heavy particle is suspended by a 1⋅5 m long string. It is given a horizontal velocity of \[\sqrt{57} \text{m/s}\] (a) Find the angle made by the string with the upward vertical when it becomes slack. (b) Find the speed of the particle at this instant. (c) Find the maximum height reached by the particle over the point of suspension. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A particle slides on the surface of a fixed smooth sphere starting from the topmost point. Find the angle rotated by the radius through the particle, when it leaves contact with the sphere.
A particle of mass m is kept on the top of a smooth sphere of radius R. It is given a sharp impulse which imparts it a horizontal speed ν. (a) Find the normal force between the sphere and the particle just after the impulse. (b) What should be the minimum value of ν for which the particle does not slip on the sphere? (c) Assuming the velocity ν to be half the minimum calculated in part, (b) find the angle made by the radius through the particle with the vertical when it leaves the sphere.
A chain of length l and mass m lies on the surface of a smooth sphere of radius R > l with one end tied to the top of the sphere. Find the gravitational potential energy of the chain with reference level at the centre of the sphere.
A chain of length l and mass m lies on the surface of a smooth sphere of radius R > l with one end tied to the top of the sphere. Suppose the chain is released and slides down the sphere. Find the kinetic energy of the chain, when it has slid through an angle θ.
A chain of length l and mass m lies on the surface of a smooth sphere of radius R > l with one end tied to the top of the sphere. Find the tangential acceleration \[\frac{d\nu}{dt}\] of the chain when the chain starts sliding down.
Give example of a situation in which an applied force does not result in a change in kinetic energy.
Two bodies of unequal mass are moving in the same direction with equal kinetic energy. The two bodies are brought to rest by applying retarding force of same magnitude. How would the distance moved by them before coming to rest compare?
A raindrop of mass 1.00 g falling from a height of 1 km hits the ground with a speed of 50 ms–1. Calculate
- the loss of P.E. of the drop.
- the gain in K.E. of the drop.
- Is the gain in K.E. equal to a loss of P.E.? If not why.
Take g = 10 ms–2
