Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A semicircular rod is joined at its end to a straight rod of the same material and the same cross-sectional area. The straight rod forms a diameter of the other rod. The junctions are maintained at different temperatures. Find the ratio of the heat transferred through a cross section of the semicircular rod to the heat transferred through a cross section of the straight rod in a given time.
उत्तर
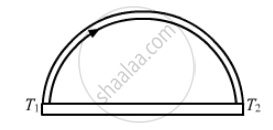
Let A be the area of cross section and K be the thermal conductivity of the material of the rod.
Let q1 be the rate of flow of heat through a semicircular rod.
Rate of flow of heat is given by
`q1 = (dQ) / dt = (K.A (T_1 - T_2 ))/(pi r)`
Let q2 be the rate of flow of heat through a straight rod.
`q_2 = (dQ)/(dt) = (KA (T_1 - T_2))/ (2r)`
Ratio of the rate of flow of heat through the 2 rods
= `(q1)/(q2) =(2r)/(pir) = 2/pi`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A tightly closed metal lid of a glass bottle can be opened more easily if it is put in hot water for some time. Explain.
Two identical rectangular strips, one of copper and the other of steel, are riveted together to form a bimetallic strip (acopper> asteel). On heating, this strip will
Find the ratio of the lengths of an iron rod and an aluminium rod for which the difference in the lengths is independent of temperature. Coefficients of linear expansion of iron and aluminium are 12 × 10–6 °C–1 and 23 × 10–6 °C–1 respectively.
An aluminium plate fixed in a horizontal position has a hole of diameter 2.000 cm. A steel sphere of diameter 2.005 cm rests on this hole. All the lengths refer to a temperature of 10 °C. The temperature of the entire system is slowly increased. At what temperature will the ball fall down? Coefficient of linear expansion of aluminium is 23 × 10–6 °C–1 and that of steel is 11 × 10–6 °C–1.
A glass window is to be fit in an aluminium frame. The temperature on the working day is 40°C and the glass window measures exactly 20 cm × 30 cm. What should be the size of the aluminium frame so that there is no stress on the glass in winter even if the temperature drops to 0°C? Coefficients of linear expansion for glass and aluminium are 9.0 × 10–6 °C–1 and 24 ×100–6°C–1 , respectively.
In a room containing air, heat can go from one place to another
A steel frame (K = 45 W m−1°C−1) of total length 60 cm and cross sectional area 0.20 cm2, forms three sides of a square. The free ends are maintained at 20°C and 40°C. Find the rate of heat flow through a cross section of the frame.
A cubical box of volume 216 cm3 is made up of 0.1 cm thick wood. The inside is heated electrically by a 100 W heater. It is found that the temperature difference between the inside and the outside surface is 5°C in steady state. Assuming that the entire electrical energy spent appears as heat, find the thermal conductivity of the material of the box.
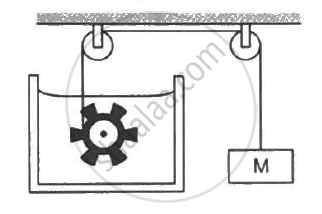
Following Figure shows water in a container having 2.0 mm thick walls made of a material of thermal conductivity 0.50 W m−1°C−1. The container is kept in a melting-ice bath at 0°C. The total surface area in contact with water is 0.05 m2. A wheel is clamped inside the water and is coupled to a block of mass M as shown in the figure. As the block goes down, the wheel rotates. It is found that after some time a steady state is reached in which the block goes down with a constant speed of 10 cm s−1 and the temperature of the water remains constant at 1.0°C. Find the mass M of the block. Assume that the heat flows out of the water only through the walls in contact. Take g = 10 m s−2.
A room has a window fitted with a single 1.0 m × 2.0 m glass of thickness 2 mm. (a) Calculate the rate of heat flow through the closed window when the temperature inside the room is 32°C and the outside is 40°C. (b) The glass is now replaced by two glasspanes, each having a thickness of 1 mm and separated by a distance of 1 mm. Calculate the rate of heat flow under the same conditions of temperature. Thermal conductivity of window glass = 1.0 J s−1 m−1°C−1 and that of air = 0.025 m-1°C-1 .
A calorimeter of negligible heat capacity contains 100 cc of water at 40°C. The water cools to 35°C in 5 minutes. The water is now replaced by K-oil of equal volume at 40°C. Find the time taken for the temperature to become 35°C under similar conditions. Specific heat capacities of water and K-oil are 4200 J kg−1 K−1 and 2100 J kg−1 K−1respectively. Density of K-oil = 800 kg m−3.
The coefficient of thermal conductivity depends upon ______.
Heat is associated with ______.
These days people use steel utensils with copper bottom. This is supposed to be good for uniform heating of food. Explain this effect using the fact that copper is the better conductor.
We would like to prepare a scale whose length does not change with temperature. It is proposed to prepare a unit scale of this type whose length remains, say 10 cm. We can use a bimetallic strip made of brass and iron each of different length whose length (both components) would change in such a way that difference between their lengths remain constant. If αiron = 1.2 × 10−5/K and αbrass = 1.8 × 10−5/K, what should we take as length of each strip?
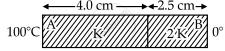
As per the given figure, two plates A and B of thermal conductivity K and 2 K are joined together to form a compound plate. The thickness of plates are 4.0 cm and 2.5 cm respectively and the area of cross-section is 120 cm2 for each plate. The equivalent thermal conductivity of the compound plate is `(1+5/alpha)`K, then the value of a will be ______.
A cylinder of radius R made of material of thermal conductivity K1 is surrounded by a cylindrical shell of inner radius R and outer radius 3R made of a material of thermal conductivity K2. The two ends of the combined system are maintained at two different temperatures. What is the effective thermal conductivity of the system?
