Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A wave of frequency 500 Hz is traveling with a speed of 350 m/s. (a) What is the phase difference between two displacements at a certain point at times 1.0 ms apart? (b) what will be the smallest distance between two points which are 45° out of phase at an instant of time?
उत्तर
Given: n = 500 Hz, v = 350 m/s
v = n × λ
∴ λ = `350/500` = 0.7 m
(a) The path difference is the distance covered v × t = 350 × 0.001 = 0.35 m at t = 1.0 ms = 0.001 s.
∴ Phase difference = `(2π)/λxx"Path difference"`
= `(2π)/0.7xx0.35` = π rad
(b) Phase difference = 45° = `π/4` rad
∴ Path difference = `λ/(2π)xx"Phase difference"`
= `0.7/(2π)xxπ/4` = 0.0875 m
संबंधित प्रश्न
A cork floating in a calm pond executes simple harmonic motion of frequency
\[\nu\] when a wave generated by a boat passes by it. The frequency of the wave is
Two waves represented by \[y = a\sin\left( \omega t - kx \right)\] and \[y = a\cos\left( \omega t - kx \right)\] \[y = a\cos\left( \omega t - kx \right)\] are superposed. The resultant wave will have an amplitude
The fundamental frequency of a string is proportional to
Two particles A and B have a phase difference of π when a sine wave passes through the region.
(a) A oscillates at half the frequency of B.
(b) A and B move in opposite directions.
(c) A and B must be separated by half of the wavelength.
(d) The displacements at A and B have equal magnitudes.
Choose the correct option:
A standing wave is produced on a string clamped at one end and free at the other. The length of the string ______.
At a prayer meeting, the disciples sing JAI-RAM JAI-RAM. The sound amplified by a loudspeaker comes back after reflection from a building at a distance of 80 m from the meeting. What maximum time interval can be kept between one JAI-RAM and the next JAI-RAM so that the echo does not disturb a listener sitting in the meeting. Speed of sound in air is 320 m s−1.
Find the change in the volume of 1.0 litre kerosene when it is subjected to an extra pressure of 2.0 × 105 N m−2 from the following data. Density of kerosene = 800 kg m−3and speed of sound in kerosene = 1330 ms−1.
A one-metre long stretched string having a mass of 40 g is attached to a tuning fork. The fork vibrates at 128 Hz in a direction perpendicular to the string. What should be the tension in the string if it is to vibrate in four loops?
In Quincke's experiment, the sound intensity has a minimum value l at a particular position. As the sliding tube is pulled out by a distance of 16.5 mm, the intensity increases to a maximum of 9 l. Take the speed of sound in air to be 330 m s−1. (a) Find the frequency of the sound source. (b) Find the ratio of the amplitudes of the two waves arriving at the detector assuming that it does not change much between the positions of minimum intensity and maximum intensity.
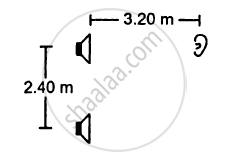
Two stereo speakers are separated by a distance of 2.40 m. A person stands at a distance of 3.20 m directly in front of one of the speakers as shown in figure. Find the frequencies in the audible range (20-2000 Hz) for which the listener will hear a minimum sound intensity. Speed of sound in air = 320 m s−1.
In a resonance column experiment, a tuning fork of frequency 400 Hz is used. The first resonance is observed when the air column has a length of 20.0 cm and the second resonance is observed when the air column has a length of 62.0 cm. (a) Find the speed of sound in air. (b) How much distance above the open end does the pressure node form?
An electronically driven loudspeaker is placed near the open end of a resonance column apparatus. The length of air column in the tube is 80 cm. The frequency of the loudspeaker can be varied between 20 Hz and 2 kHz. Find the frequencies at which the column will resonate. Speed of sound in air = 320 m s−1.
A piston is fitted in a cylindrical tube of small cross section with the other end of the tube open. The tube resonates with a tuning fork of frequency 512 Hz. The piston is gradually pulled out of the tube and it is found that a second resonance occurs when the piston is pulled out through a distance of 32.0 cm. Calculate the speed of sound in the air of the tube.
A U-tube having unequal arm-lengths has water in it. A tuning fork of frequency 440 Hz can set up the air in the shorter arm in its fundamental mode of vibration and the same tuning fork can set up the air in the longer arm in its first overtone vibration. Find the length of the air columns. Neglect any end effect and assume that the speed of sound in air = 330 m s−1.
A Kundt's tube apparatus has a copper rod of length 1.0 m clamped at 25 cm from one of the ends. The tube contains air in which the speed of sound is 340 m s−1. The powder collects in heaps separated by a distance of 5.0 cm. Find the speed of sound waves in copper.
Calculate the frequency of beats produced in air when two sources of sound are activated, one emitting a wavelength of 32 cm and the other of 32.2 cm. The speed of sound in air is 350 m s−1.
A person riding a car moving at 72 km h−1 sound a whistle emitting a wave of frequency 1250 Hz. What frequency will be heard by another person standing on the road (a) in front of the car (b) behind the car? Speed of sound in air = 340 m s−1.
A bat emitting an ultrasonic wave of frequency 4.5 × 104 Hz flies at a speed of 6 m s−1between two parallel walls. Find the fractional heard by the bat and the beat frequencies heard by the bat and the beat frequency between the two. The speed of sound is 330 m s−1.
A bullet passes past a person at a speed of 220 m s−1. Find the fractional change in the frequency of the whistling sound heard by the person as the bullet crosses the person. Speed of sound in air = 330 m s−1.
A source emitting sound at frequency 4000 Hz, is moving along the Y-axis with a speed of 22 m s−1. A listener is situated on the ground at the position (660 m, 0). Find the frequency of the sound received by the listener at the instant the source crosses the origin. Speed of sound in air = 330 m s−1.
A source emitting a sound of frequency v is placed at a large distance from an observer. The source starts moving towards the observer with a uniform acceleration a. Find the frequency heard by the observer corresponding to the wave emitted just after the source starts. The speed of sound in the medium is v.
The speed of sound in hydrogen is 1270 m/s. The speed of sound in the mixture of oxygen and hydrogen in which they are mixed in 1:4 ratio is
A metallic wire of 1 m length has a mass of 10 × 10−3 kg. If the tension of 100 N is applied to a wire, what is the speed of the transverse wave?
The speed of a transverse wave in an elastic string is v0. If the tension in the string is reduced to half, then the speed of the wave is given by:
Change in temperature of the medium changes ______.
Two tuning forks having frequencies 320 Hz and 340 Hz are sounded together to produce sound waves. The velocity of sound in air is 340 m/s. Find the difference in wavelength of these waves.
