Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The fundamental frequency of a string is proportional to
पर्याय
inverse of its length
the diameter
the tension
the density.
उत्तर
inverse of its length
The relation between wave speed and the length of the string is given by
\[v = \frac{1}{2l}\sqrt{\frac{F}{\mathrm{\mu}}}\]
where
l is the length of the string
F is the tension
μ linear mass density
From the above relation, we can say that the fundamental frequency of a string is proportional to the inverse of the length of the string.
\[v \propto \frac{1}{l}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A cork floating in a calm pond executes simple harmonic motion of frequency
\[\nu\] when a wave generated by a boat passes by it. The frequency of the wave is
Choose the correct option:
A standing wave is produced on a string clamped at one end and free at the other. The length of the string ______.
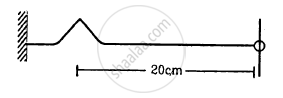
A string of linear mass density 0⋅5 g cm−1 and a total length 30 cm is tied to a fixed wall at one end and to a frictionless ring at the other end (See figure). The ring can move on a vertical rod. A wave pulse is produced on the string which moves towards the ring at a speed of 20 cm s−1. The pulse is symmetric about its maximum which is located at a distance of 20 cm from the end joined to the ring. (a) Assuming that the wave is reflected from the ends without loss of energy, find the time taken by the string to region its shape. (b) The shape of the string changes periodically with time. Find this time period. (c) What is the tension in the string?
Find the change in the volume of 1.0 litre kerosene when it is subjected to an extra pressure of 2.0 × 105 N m−2 from the following data. Density of kerosene = 800 kg m−3and speed of sound in kerosene = 1330 ms−1.
In Quincke's experiment the sound detected is changed from a maximum to a minimum when the sliding tube is moved through a distance of 2.50 cm. Find the frequency of sound if the speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1.
A closed organ pipe can vibrate at a minimum frequency of 500 Hz. Find the length of the tube. Speed of sound in air = 340 m s−1.
In a resonance column experiment, a tuning fork of frequency 400 Hz is used. The first resonance is observed when the air column has a length of 20.0 cm and the second resonance is observed when the air column has a length of 62.0 cm. (a) Find the speed of sound in air. (b) How much distance above the open end does the pressure node form?
An open organ pipe has a length of 5 cm. (a) Find the fundamental frequency of vibration of this pipe. (b) What is the highest harmonic of such a tube that is in the audible range? Speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1 and the audible range is 20-20,000 Hz.
Calculate the frequency of beats produced in air when two sources of sound are activated, one emitting a wavelength of 32 cm and the other of 32.2 cm. The speed of sound in air is 350 m s−1.
A bat emitting an ultrasonic wave of frequency 4.5 × 104 Hz flies at a speed of 6 m s−1between two parallel walls. Find the fractional heard by the bat and the beat frequencies heard by the bat and the beat frequency between the two. The speed of sound is 330 m s−1.
A small source of sound vibrating at frequency 500 Hz is rotated in a circle of radius 100/π cm at a constant angular speed of 5.0 revolutions per second. A listener situation situates himself in the plane of the circle. Find the minimum and the maximum frequency of the sound observed. Speed of sound in air = 332 m s−1.
Two trains are travelling towards each other both at a speed of 90 km h−1. If one of the trains sounds a whistle at 500 Hz, what will be the apparent frequency heard in the other train? Speed of sound in air = 350 m s−1.
A car moving at 108 km h−1 finds another car in front it going in the same direction at 72 km h−1. The first car sounds a horn that has a dominant frequency of 800 Hz. What will be the apparent frequency heard by the driver in the front car? Speed of sound in air = 330 m s−1.
A source emitting a sound of frequency v is placed at a large distance from an observer. The source starts moving towards the observer with a uniform acceleration a. Find the frequency heard by the observer corresponding to the wave emitted just after the source starts. The speed of sound in the medium is v.
A wave of frequency 500 Hz is traveling with a speed of 350 m/s. (a) What is the phase difference between two displacements at a certain point at times 1.0 ms apart? (b) what will be the smallest distance between two points which are 45° out of phase at an instant of time?
The speed of a transverse wave in an elastic string is v0. If the tension in the string is reduced to half, then the speed of the wave is given by:
