Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
and ```vecE` and `vecB`denote electric and magnetic fields in a frame S and `vecE`→ and `vecB` in another frame S' moving with respect to S at a velocity `vecV` Two of the following equations are wrong. Identify them.
(a) `B_y^, = B_y + (vE_z)/c^2`
(b) `E_y^' = E_y - (vB_z)/(c^2)`
`(c) Ey = By + vE_z`
`(d) E_y = E_y + vB_z`
उत्तर
(b) `E_y^' = E_y - (vB_z)/(c^2)`
`(c) Ey = By + vE_z`
Electric force due to a charged particle is q E and magnetic force is q V B.
We can sort out the two wrong equations using dimensional analysis. Now, equating the above two forces. we get:
E = V B
Hence, analysing the answers using dimensional analysis, we see that the second term on the RHS of the equations (b) and (c) are not dimensionally correct. Thus, the options (b) and (c) are wrong.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The figure shows three infinitely long straight parallel current carrying conductors. Find the
(i) magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at point A lying on conductor 1,
(ii) magnetic force on conductor 2.

Two long straight parallel conductors 'a' and 'b', carrying steady currents Ia and Ib are separated by a distance d. Write the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field produced by the conductor 'a' at the points along the conductor 'b'. If the currents are flowing in the same direction, what is the nature and magnitude of the force between the two conductors?
An electron beam projected along the positive x-axis deflects along the positive y-axis. If this deflection is caused by a magnetic field, what is the direction of the field? Can we conclude that the field is parallel to the z-axis?
A charged particle goes undeflected in a region containing an electric and a magnetic field. It is possible that
(a) `vecE" || "vecB , vecv" || " vec E `
(b) `vecE "is not parallel" vecB`
(c) `vecv " || " vecB but vecv "is not parallel"`
(d) `vecE" || " vecB but vecv "is not parallel"`
A long, straight wire carries a current along the z-axis, One can find two points in the x−y plane such that
(a) the magnetic fields are equal
(b) the directions of the magnetic fields are the same
(c) the magnitudes of the magnetic fields are equal
(d) the field at one point is opposite to that at the other point.
A long, straight wire of radius r carries a current i and is placed horizontally in a uniform magnetic field B pointing vertically upward. The current is uniformly distributed over its cross section. (a) At what points will the resultant magnetic field have maximum magnitude? What will be the maximum magnitude? (b) What will be the minimum magnitude of the resultant magnetic field?
A hypothetical magnetic field existing in a region is given by `vecB = B_0 vece` where `vece`_r denotes the unit vector along the radial direction. A circular loop of radius a, carrying a current i, is placed with its plane parallel to the x−y plane and the centre at (0, 0, d). Find the magnitude of the magnetic force acting on the loop.
Figure shows two parallel wires separated by a distance of 4.0 cm and carrying equal currents of 10 A along opposite directions. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the points A1, A2, A3.

Two parallel wires carry equal currents of 10 A along the same direction and are separated by a distance of 2.0 cm. Find the magnetic field at a point which is 2.0 cm away from each of these wires.
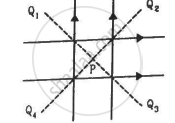
Four long, straight wires, each carrying a current of 5.0 A, are placed in a plane as shown in figure. The points of intersection form a square of side 5.0 cm.
(a) Find the magnetic field at the centre P of the square.
(b) Q1, Q2, Q3, and Q4, are points situated on the diagonals of the square and at a distance from P that is equal to the diagonal of the square. Find the magnetic fields at these points.
A straight, how wire carries a current of 20 A. Another wire carrying equal current is placed parallel to it. If the force acting on a length of 10 cm of the second wire is 2.0 × 10−5 N, what is the separation between them?
If a current I is flowing in a straight wire parallel to x-axis and magnetic field is there in the y-axis then, ______.
Do magnetic forces obey Newton’s third law. Verify for two current elements dl1 = dlî located at the origin and dl2 = dlĵ located at (0, R, 0). Both carry current I.
Two long straight parallel conductors carrying currents I1 and I2 are separated by a distance d. If the currents are flowing in the same direction, show how the magnetic field produced by one exerts an attractive force on the other. Obtain the expression for this force and hence define 1 ampere.
Two long straight parallel current-carrying conductors are kept ‘a’ distant apart in the air. The direction of current in both the conductors is the same. Find the magnitude of force per unit length and the direction of the force between them. Hence define one ampere.
