Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
Define the term wavefront. Using Huygen's wave theory, verify the law of reflection.
उत्तर
A wavefront is defined as the locus of all points having the same phase at a given instant of time.
Derivation of Law of reflection:
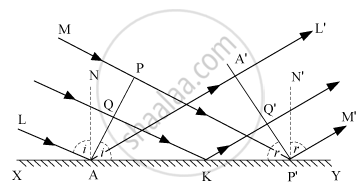
Consider any point Q on the incident wavefront PA.
When the disturbance from P on incident wavefront reaches point P', the disturbance from point Q reaches Q'.
If c is the velocity of light, then the time taken by light to go from point Q to Q'(via point K) is given by,
`r = "QK"/c + "KQ'"/c` ...(i)
In right-angled ΔAQK,
∠QAK = ∠i
∴ QK = AK sin i
In right-angled, ΔKQ'P'
∠Q'P'K = r
∴ KQ' = KP' sin r
Substituting these values in equation (1),
`t = ("AK" sin i)/(c) +("KP"' sin r)/(c)`
`t = ("AK" sin i + ("AP"' - "AK") sinr)/(c) ...(∵ "KP"' = "AP"' - "AK"')`
`t = ("AP"' sinr + "AK"(sin i - sin r))/(c)` ....(ii)
The rays from different points on incident wavefront will take the same time to reach the corresponding points on the reflected wavefront, if ‘t’ given by equation (ii) is independent of AK.
∴ AK (sin i − sin r) = 0
sin i − sin r = 0
sin i = sin r
i = r
i.e., the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Also, the incident ray (LA or MP'), reflected ray (AA'L' or P'M'), and the normal (AN) − all lie in the same plane.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the shape of the wavefront in the following case?
Light diverging from a point source.
State Huygen's principle.
Use Huygens' principle to verify the laws of refraction.
The refractive indices of water and diamond are `4/3` and 2.42 respectively. Find the speed of light in water and diamond. (c = 3x108 m/s)
When the width of the slit is made double the original width, how would this affect the size and intensity of the central diffraction band?
State Huygens’s principle. Show, with the help of a suitable diagram, how this principle is used to obtain the diffraction pattern by a single slit.
Draw a plot of intensity distribution and explain clearly why the secondary maxima becomes weaker with increasing order (n) of the secondary maxima.
Huygen's conception of secondary waves ______.
According to Huygens's principle, the amplitude of secondary wavelets is ______.
How is a wavefront different from a ray?
Represent diagrammatically how the incident planar wavefronts of wavelength λ pass through an aperture of size d, when d is approximately equal to λ.
