Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
Draw geometric isomers and enantiomers of the following complex.
[Pt(en)3]4⊕
उत्तर
[Pt(en)3]4+ shows only enantiomers as follows:

संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the structural formula and IUPAC names of all possible isomers of the compound with molecular formula C3H8O.
Give one chemical test as an evidence to show that [Co (NH3)5Cl] are ionisation isomers.
Answer the following question.
Draw isomers of the following
Ru(NH3)4Cl2
Answer the following question.
Draw geometric isomers and enantiomers of the following complex.
[Pt(en)2ClBr]2⊕
Define the term Hydrated isomers.
Draw the geometrical isomers of the following complexes [Pt(NH3)(H2O)Cl2].
Draw optical isomers of [Co(en)3]3+.
Explain optical isomerism in coordination compounds with an example.
What are hydrate isomers? Explain with an example.
Which would exhibit coordination isomerism?
How many isomers are possible for an alkane having molecular formula C5H12?
The number of geometrical isomers of [CrCl2(en)2]+ is ____________.
Which of the following is NOT an isomer of n-hexane?
____________ isomers are formed when the ligand has two different donor atoms.
Which of the following has zero dipole moment?
Indicate the complex ion which shows geometrical isomerism.
The relationship between compound (i) and (ii) is
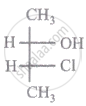 |
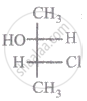 |
| (i) | (ii) |
Which of the following does not show optical isomerism?
Which of the following compound show optical isomerism?
Which among the following solid is a non-polar solid?
The compounds [PtCl2(NH3)4]Br2 and [PtBr2(NH3)4]Cl2 constitutes a pair of ______.
Define Distereoisomers.
Give trans isomer of [Co(NH3)4Cl2]⊕.
Indicate the type of isomerism exhibited by the following complex and draw the structures for this isomer:
\[\ce{[Pt(NH3)(H2O)Cl2]}\]
The co-ordination number of Co3+ ion in the complex [Co(NH3)4Cl2]⊕ is ______.
Name the type of isomerism exhibited by the following pair of compound:
\[\ce{[Pt(NH3)4Cl2]Br2 and [Pt(NH3)4 Br2]Cl2}\]
Three organic compounds A, B and C are non cyclic functional isomers of carbonyl compounds with molecular formula C4H8O. Isomers A and C give positive Tollen’s test while compound B does not give positive Tollen’s test but gives positive iodoform test. Compounds A and B on reduction with Zn amalgam and conc. HCl give the same product.
- Write the structures of the compounds A, B and C.
- Out of the compounds A, B and C, which one will be the least reactive towards addition of HCN.
