Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
Draw isomers of the following
[Cr(en2)Br2]⊕
उत्तर
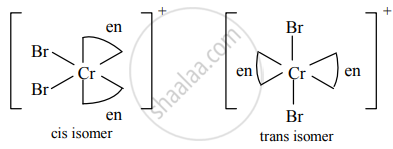
Cis and trans isomers of [Cr(en2)Br2]⊕
a. Cis and trans isomers of [Cr(en2)Br2]+
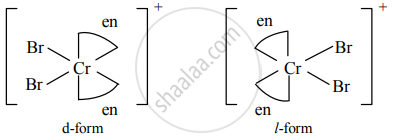
b. Optical isomers of [Cr(en2)Br2]+
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
List various types of isomerism possible for coordination compounds, giving an example of each.
Out of 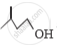 and
and 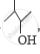 , which one is optically active and why ?
, which one is optically active and why ?
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
Consider the complexes \[\ce{[Cu(NH3)4][PtCl4] and [Pt(NH3)4] [CuCl4]}\]. What type of isomerism these two complexes exhibit?
Answer in brief.
What are ionization isomers ? Give an example.
Draw isomers of the following.
\[\ce{Pt(NH3)2ClNO2}\]
Answer the following question.
Draw isomers of the following
Ru(NH3)4Cl2
Write the type of isomerism exhibited by [Co(NH3)5(NO2)]2+ and [Co(NH3)5ONO]2+ pair of complex ion.
Which type of isomerism is exhibited by [Pt(NH3)2Cl2]?
How many geometrical isomers are possible for \[\ce{[Pt(Py)(NH3)(Br)(Cl)]}\]?
Fac-mer isomerism is shown by
The number of geometrical isomers of [CrCl2(en)2]+ is ____________.
What type of isomerism is present between (I) [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3 and (II) [Cr(H2O)5Cl]Cl2.H2O?
Assertion: Complexes of MX6 and MX5L type (X and L are unidentate) do not show geometrical isomerism.
Reason: Geometrical isomerism is not shown by complexes of coordination number 6.
The relationship between compound (i) and (ii) is
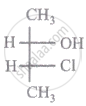 |
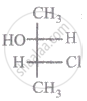 |
| (i) | (ii) |
Which of the following are isostructural pairs?
(A) \[\ce{SO^{2-}4}\] and \[\ce{CrO^{2-}4}\]
(B) SiCl4 and TiCl4
(C) NH3 and \[\ce{NO^-3}\]
(D) BCl3 and BrCl3
Which compound would exhibit optical isomers?
The number of geometrical isomers of \[\ce{[Co(NH3)3 (NO3)3]}\] are ______.
The compounds [PtCl2(NH3)4]Br2 and [PtBr2(NH3)4]Cl2 constitutes a pair of ______.
Write structures for geometrical isomers of diamminebromochloroplatinum (II).
What are structural isomers or constitutional isomers?
Match the pairs in column I (pairs of isomers) and column II (types of isomers)
| Column I (Pairs of isomers) |
Column II (Types of isomers) |
| (A) [Cr(H2O)5Cl]Cl2.H2O and [Cr(H2O)4Cl2]Cl.2H2O | (i) Ionization isomers |
| (B) [Co(en)2(NO2)2]+ and [Co(en)2(ONO2)]+ | (ii) Hydrate isomers |
| (C) [Co(NH3)6] [Cr(CN)6] and [Cr(NH3)6] [Co(CN)6] | (iii) Linkage isomers |
| (D) [Pt(NH3)4Cl2] Br2 and [Pt(NH3)4Br2]Cl2 | (iv) Coordination isomers |
Draw the structure of cis isomers of Pt(NH3)2Cl2.
Name the type of isomerism exhibited by the following pair of compound:
\[\ce{[Co(NH3)5 [ONO]Cl2 and [Co(NH3)5(NO2)]Cl2}\]
Name the type of isomerism exhibited by the following pair of compound:
\[\ce{[Pt(NH3)4Cl2]Br2 and [Pt(NH3)4 Br2]Cl2}\]
Give a chemical test to show that \[\ce{[Co(NH3)5Cl]SO4}\] and \[\ce{[Co(NH3)5SO4]CI}\] are ionisation isomers.
Which one of the following complex ions has geometrical isomers?
Three organic compounds A, B and C are non cyclic functional isomers of carbonyl compounds with molecular formula C4H8O. Isomers A and C give positive Tollen’s test while compound B does not give positive Tollen’s test but gives positive iodoform test. Compounds A and B on reduction with Zn amalgam and conc. HCl give the same product.
- Write the structures of the compounds A, B and C.
- Out of the compounds A, B and C, which one will be the least reactive towards addition of HCN.
