Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
List various types of isomerism possible for coordination compounds, giving an example of each.
उत्तर
(i) Geometric isomerism: This type of isomerism is common in heteroleptic complexes. It arises due to the different possible geometric arrangements of the ligands. For example:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..}\ce{Cl}\phantom{.....}\ce{NH3}\phantom{}\\
\backslash\phantom{...}/\\
\ce{Pt}\\
/\phantom{...}\backslash\\
\ce{\underset{cis}{\phantom{..}Cl\phantom{.....}NH3}}
\end{array}\]
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..}\ce{Cl}\phantom{.....}\ce{NH3}\phantom{}\\
\phantom{}\backslash\phantom{...}/\\
\ce{Pt}\\
/\phantom{...}\backslash\phantom{}\\
\ce{\underset{trans}{NH3\phantom{....}Cl\phantom{..}}}
\end{array}\]
(ii) Optical isomerism: This type of isomerism arises in chiral molecules. Isomers are mirror images of each other and are non-superimposable.
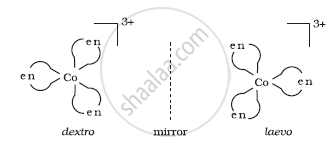
(iii) Linkage isomerism: This type of isomerism is found in complexes that contain ambidentate ligands. For example, [Co(NH3)5(NO2)]Cl2, which is obtained as a red form and [Co(NH3)5(ONO)]Cl2 obtained as a yellow form.
(iv) Coordination isomerism: This type of isomerism arises when the ligands are interchanged between cationic and anionic entities of different metal ions present in the complex. For example, [Co(NH3)6] [Cr(CN)6] and [Cr(NH3)6] [Co(CN)6].
(v) Ionization isomerism: This type of isomerism arises when a counter ion replaces a ligand within the coordination sphere. Thus, complexes that have the same composition but furnish different ions when dissolved in water are called ionization isomers. For example, [Co(NH3)5(SO4)]Br and [Co(NH3)5Br]SO4.
(vi) Solvate isomerism: Solvate isomers differ by whether or not the solvent molecule is directly bonded to the metal ion or merely present as a free solvent molecule in the crystal lattice. For example, [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3 (violet) and [Cr(H2O)5Cl]Cl2.H2O (grey-green).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why dextro and laevo rotatory isomers of Butan-2-ol are difficult to separate by fractional distillation?
Choose the most correct option.
Which of the following complexes exist as cis and trans isomers?
1. [Cr(NH3)2Cl4]-
2. [Co(NH3)5Br]2⊕
3. [PtCl2Br2]2- (square planar)
4. [FeCl2(NCS)2]2- (tetrahedral)
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
Predict whether the [Cr(en)2(H2O)2]3+ complex is chiral. Write the structure of its enantiomer.
The pair [Co(NH3)5(SO4)]Br and [Co(NH3)5Br]SO4 exhibits ____________ isomerism
Write the type of isomerism exhibited by [Co(NH3)5(NO2)]2+ and [Co(NH3)5ONO]2+ pair of complex ion.
Which one of the following pairs represents linkage isomers?
The term anomers of glucose refer to ____________.
How many isomers are possible for an alkane having molecular formula C5H12?
____________ isomers are formed when the ligand has two different donor atoms.
Which of the following compound show optical isomerism?
Which of the following shows maximum number of isomers?
\[\ce{CH3CH2COO- Na+ ->[NaOH, + ?][Heat] CH3CH3 + Na2CO3}\]
Consider the above reaction and identify the missing reagent/chemical.
Which of the following are isostructural pairs?
(A) \[\ce{SO^{2-}4}\] and \[\ce{CrO^{2-}4}\]
(B) SiCl4 and TiCl4
(C) NH3 and \[\ce{NO^-3}\]
(D) BCl3 and BrCl3
The one that is not expected to show isomerism is ______.
Which among the following solid is a non-polar solid?
Explain the ionisation isomers.
Draw the structure of trans isomers of Pt(NH3)2Cl2.
Name the type of isomerism exhibited by the following pair of compound:
\[\ce{[Pt(NH3)4Cl2]Br2 and [Pt(NH3)4 Br2]Cl2}\]
Three organic compounds A, B and C are non cyclic functional isomers of carbonyl compounds with molecular formula C4H8O. Isomers A and C give positive Tollen’s test while compound B does not give positive Tollen’s test but gives positive iodoform test. Compounds A and B on reduction with Zn amalgam and conc. HCl give the same product.
- Write the structures of the compounds A, B and C.
- Out of the compounds A, B and C, which one will be the least reactive towards addition of HCN.
