Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
\[\ce{[CO(H2O)6]^2+ (aq) (pink) + 4Cl- (aq) <=> [CoCl4]^2- (aq) (blue) + 6 H2O (l)}\]
In the above reaction at equilibrium, the reaction mixture is blue in colour at room temperature. On cooling this mixture, it becomes pink in color. On the basis of this information, which one of the following is true?
पर्याय
∆H > 0 for the forward reaction
∆H = 0 for the reverse reaction
∆H < 0 for the forward reaction
Sign of the ∆H cannot be predicted based on this information
उत्तर
∆H > 0 for the forward reaction
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the equilibrium,
\[\ce{2A(g) <=> 2B(g) + C2(g)}\]
the equilibrium concentrations of A, B and C2 at 400 K are 1 × 10–4 M, 2.0 × 10–3 M, 1.5 × 10–4 M respectively. The value of KC for the equilibrium at 400 K is
The equilibrium constants of the following reactions are:
\[\ce{N2 + 3H2 <=> 2NH3}\]; K1
\[\ce{N2 + O2 <=> 2NO}\]; K2
\[\ce{H2 + 1/2O2 <=> H2O}\]; K3
The equilibrium constant (K) for the reaction;
\[\ce{2NH3 + 5/2 O2 <=> 2NO + 3H2O}\], will be
For a given reaction at a particular temperature, the equilibrium constant has a constant value. Is the value of Q also constant? Explain.
When the numerical value of the reaction quotient (Q) is greater than the equilibrium constant, in which direction does the reaction proceed to reach equilibrium?
For the reaction, \[\ce{A2(g) + B2(g) <=> 2AB(g); \Delta H}\] is -ve.
the following molecular scenes represent differenr reaction mixture. (A-green, B-blue)
| Closed ← |
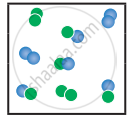 |
 |
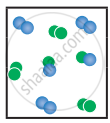 |
| System | At equilibrium | (x) | (y) |
- Calculate the equilibrium constant Kp and (Kc).
- For the reaction mixture represented by scene (x), (y) the reaction proceed in which directions?
- What is the effect of an increase in pressure for the mixture at equilibrium?
Derive a general expression for the equilibrium constant Kp and Kc for the reaction, \[\ce{3H2(g) + N2(g) <=> 2NH3(g)}\].
What is the effect of added Inert gas on the reaction at equilibrium?
For the reaction
\[\ce{SrCO3(s) <=> SrO(s) + CO2(g)}\]
the value of equilibrium constant Kp = 2.2 × 10-4 at 1002 K. Calculate Kc for the reaction.
At particular temperature Kc = 4 × 10-2 for the reaction, \[\ce{H2S (g) <=> H2(g) +1/2 S2(g)}\]. Calculate the Kc for the following reaction.
\[\ce{2H2S (g) <=> 2H2 (g) + S2 (g)}\]
At particular temperature Kc = 4 × 10-2 for the reaction, \[\ce{H2S (g) <=> H2(g) +1/2 S2(g)}\]. Calculate the Kc for the following reaction.
\[\ce{3H2S (g) <=> 3H2 (g) + 3/2 S2 (g)}\]
