Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Cell equation: \[\ce{A + 2B^- -> A^{2+} + 2B}\]
\[\ce{A^{2+} + 2e^- -> A}\] E0 = +0.34 V and log10 k = 15.6 at 300 K for cell reactions find E0 for \[\ce{B^+ + e^- -> B}\]
पर्याय
0.80
1.26
– 0.54
– 10.94
उत्तर
0.80
Explanation:
\[\ce{A + 2B^- -> A^{2+} + 2B}\]
Half reaction anode: \[\ce{A -> A^2+ + 2e^-}\]
`"E"_"ox"^0` = –0.34 V ........[Given: \[\ce{A^{2+} + 2e^- -> A}\] E0 = +0.34 V]
Cathode: \[\ce{2B^+ + 2e^- -> 2B}\] `"E"_"red"^0` = ?
log10 K = 156; T = 300 K; n = 2;
F = 96500 C
R = 8.314 JK−1 mol−1
∆G° = – 2.303 RT log K
∴ nFE° = – 2.303 RT log K
`"E"_"cell"^0 = (2.303 "RT" log "K")/("nF")`
= `(2.303 xx 8.314 xx 300 xx 15.6)/(2 xx 96500)`
= 0.4643 V
`"E"_"cell"^0 = "E"_"ox"^0 + "E"_"red"^0`
`"E"_"red"^0 = "E"_"cell"^0 + "E"_"ox"^0`
∴ 0.4643 – (–0.34)
= 0.4643 + 0.34
= 0.8043
= 0.80 V
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Among Zn and Cu, which would occur more readily in nature as metal and which as an ion?
Define the following term:
Fuel cell
Assertion: pure iron when heated in dry air is converted with a layer of rust.
Reason: Rust has the compositionFe3O4.
Consider the change in the oxidation state of Bromine corresponding to different emf values as shown in the diagram below:
\[\ce{BrO^-_4 ->[1.82 V] BrO^-_3 ->[1.5 V] HBrO ->[1.595 V] Br2 ->[1.0652 V] Br^-}\]
Then the species undergoing disproportionation is
Electrode potential for Mg electrode varies according to the equation
`E_(Mg^(2+) | Mg) = E_(Mg^(2+) | Mg)^Θ - 0.059/2 log 1/([Mg^(2+)])`. The graph of `E_(Mg^(2+) | Mg)` vs `log [Mg^(2+)]` is ______.
Which of the following statement is not correct about an inert electrode in a cell?
What is electrode potential?
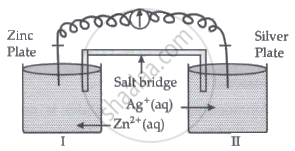
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow:
|
Oxidation-reduction reactions are commonly known as redox reactions. They involve transfer of electrons from one species to another. In a spontaneous reaction, energy is released which can be used to do useful work. The reaction is split into two half-reactions. Two different containers are used and a wire is used to drive the electrons from one side to the other and a Voltaic/Galvanic cell is created. It is an electrochemical cell that uses spontaneous redox reactions to generate electricity. A salt bridge also connects to the half-cells. The reading of the voltmeter gives the cell voltage or cell potential or electromotive force. If \[\ce{E^0_{cell}}\] is positive the reaction is spontaneous and if it is negative the reaction is non-spontaneous and is referred to as electrolytic cell. Electrolysis refers to the decomposition of a substance by an electric current. One mole of electric charge when passed through a cell will discharge half a mole of a divalent metal ion such as Cu2+. This was first formulated by Faraday in the form of laws of electrolysis.
|
- Is silver plate the anode or cathode? (1)
- What will happen if the salt bridge is removed? (1)
- When does electrochemical cell behaves like an electrolytic cell? (1)
- (i) What will happen to the concentration of Zn2+ and Ag+ when Ecell = 0. (1)
(ii) Why does conductivity of a solution decreases with dilution? (1)
OR
The molar conductivity of a 1.5 M solution of an electrolyte is found to be 138.9 S cm2mol-1. Calculate the conductivity of this solution. (2)
In a solution of CuSO4, how much time will be required to precipitate 2 g copper by 0.5 ampere current?
The two half cell reaction of an electrochemical cell is given as
\[\ce{Ag+ + e- -> Ag}\], `"E"_("Ag"^+//"Ag")^circ` = - 0.3995 V
\[\ce{Fe^{2+} -> Fe^{3+} + e-}\], `"E"_("Fe"^{3+}//"Fe")^{2+}` = - 0.7120 V
The value of EMF will be ______.