Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
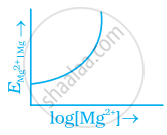
Electrode potential for Mg electrode varies according to the equation
`E_(Mg^(2+) | Mg) = E_(Mg^(2+) | Mg)^Θ - 0.059/2 log 1/([Mg^(2+)])`. The graph of `E_(Mg^(2+) | Mg)` vs `log [Mg^(2+)]` is ______.
पर्याय
उत्तर
Electrode potential for Mg electrode varies according to the equation
`E_(Mg^(2+) | Mg) = E_(Mg^(2+) | Mg)^Θ - 0.059/2 log 1/([Mg^(2+)])`. The graph of `E_(Mg^(2+) | Mg)` vs `log [Mg^(2+)]` is a straignt line with a positive slope and intercept `E_((Mg^(2+))/(Mg)`.
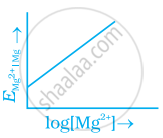
Explanation:
`E_(Mg^(2+) | mg) = E_(Mg^(2+) | Mg)^Θ - 0.059/2 log [Mg^(2+)]`
Compare this equation with the equation of straingt line y = mx + c.
The graph of `E_(Mg^(2+) | Mg)` versus `log [Mg^(2+)]` is a straignt line with a positive slope and intercept `E_((Mg^(2+))/(Mg)`.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If 'I' stands for the distance between the electrodes and 'a' stands for the area of cross-section of the electrode, `"l"/"a"` refers to ____________.
At 25°C, the emf of the following electrochemical cell.
\[\ce{Ag_{(s)} | Ag^+ (0.01 M) | | Zn^{2+} {(0.1 M)} | Zn_{(s)}}\] will be:
(Given \[\ce{E^0_{cell}}\] = −1.562 V)
Assertion: pure iron when heated in dry air is converted with a layer of rust.
Reason: Rust has the compositionFe3O4.
Cell equation: \[\ce{A + 2B^- -> A^{2+} + 2B}\]
\[\ce{A^{2+} + 2e^- -> A}\] E0 = +0.34 V and log10 k = 15.6 at 300 K for cell reactions find E0 for \[\ce{B^+ + e^- -> B}\]
Define anode
Describe the construction of Daniel cell. Write the cell reaction.
Why is anode in galvanic cell considered to be negative and cathode positive electrode?
Two metals M1 and M2 have reduction potential values of −xV and +yV respectively. Which will liberate H2 and H2SO4.
`E_(cell)^Θ` for some half cell reactions are given below. On the basis of these mark the correct answer.
(a) \[\ce{H^{+} (aq) + e^{-} -> 1/2 H_2 (g); E^Θ_{cell} = 0.00V}\]
(b) \[\ce{2H2O (1) -> O2 (g) + 4H^{+} (aq) + 4e^{-}; E^Θ_{cell} = 1.23V}\]
(c) \[\ce{2SO^{2-}_{4} (aq) -> S2O^{2-}_{8} (aq) + 2e^{-}; E^Θ_{cell} = 1.96V}\]
(i) In dilute sulphuric acid solution, hydrogen will be reduced at cathode.
(ii) In concentrated sulphuric acid solution, water will be oxidised at anode.
(iii) In dilute sulphuric acid solution, water will be oxidised at anode.
(iv) In dilute sulphuric acid solution, \[\ce{SO4^{2-}}\] ion will be oxidised to tetrathionate ion at anode.
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow:
|
Oxidation-reduction reactions are commonly known as redox reactions. They involve transfer of electrons from one species to another. In a spontaneous reaction, energy is released which can be used to do useful work. The reaction is split into two half-reactions. Two different containers are used and a wire is used to drive the electrons from one side to the other and a Voltaic/Galvanic cell is created. It is an electrochemical cell that uses spontaneous redox reactions to generate electricity. A salt bridge also connects to the half-cells. The reading of the voltmeter gives the cell voltage or cell potential or electromotive force. If \[\ce{E^0_{cell}}\] is positive the reaction is spontaneous and if it is negative the reaction is non-spontaneous and is referred to as electrolytic cell. Electrolysis refers to the decomposition of a substance by an electric current. One mole of electric charge when passed through a cell will discharge half a mole of a divalent metal ion such as Cu2+. This was first formulated by Faraday in the form of laws of electrolysis.
|
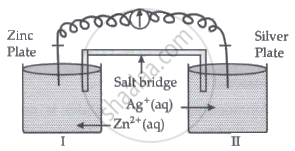
- Is silver plate the anode or cathode? (1)
- What will happen if the salt bridge is removed? (1)
- When does electrochemical cell behaves like an electrolytic cell? (1)
- (i) What will happen to the concentration of Zn2+ and Ag+ when Ecell = 0. (1)
(ii) Why does conductivity of a solution decreases with dilution? (1)
OR
The molar conductivity of a 1.5 M solution of an electrolyte is found to be 138.9 S cm2mol-1. Calculate the conductivity of this solution. (2)