Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Comment on Acini of thyroid gland.
उत्तर
The thyroid gland is a bilobed endocrine gland. Each lobe is made up of many lobules. The lobules consist of follicles called acini. Each acinus is lined with glandular, cuboidal, or squamous epithelial cells. The lumen of the acinus is filled with colloid, a thick glycoprotein mixture consisting of thyroglobulin molecules.
संबंधित प्रश्न
| Hormones | Target gland |
| Thyrotrophin (TSH) | ______ |
| Hormones | Target gland |
| Gonadotrophins (LH, FSH) | ______ |
| Hormones | Target gland |
| Melanotrophin (MSH | ______ |
Give an example of a progestational hormone.
What is the difference between an exocrine gland and an endocrine gland?
Define the following:
Endocrine glands
Mention which of the statements are true (T) and which are false (F). Give reason in support of your answer.
Harmones ‘obey’ the commands like ‘enough, slow down or ‘two little, speed up’
Mention any two differences between a hormone and an enzyme.
Do you agree with the statement – “ All hormones are chemical signals”? Yes / No. Justify your answer.
Compare the hormonal response with the nervous response with respect to their speed, transmission and the general nature of changes brought about.
Identify the ODD term in each set and name the CATEGORY to which the remaining three belong :
Example : glucose, starch, cellulose, calcium
Odd term : calcium
Category : others are different types of carbohydrates
Addison’s disease, Cushing’s Syndrome, Acromegaly, Leukemia
The diagram give below represents an endocrine gland in the human body. Study the diagram and answer the following questions: 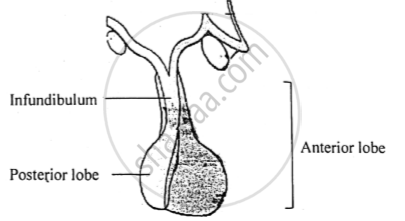
Explain the term ‘Hormone’. What is the role of Tropic hormones in the human body?
Which one of the following statement is true/ false?
Islets of Langerhans are found in the brain.
Which one of the following statement is true/ false?
The pituitary gland is both exocrine and endocrine in function.
Define the following:
Hypersecretion
Name the hormones secreted by the following glands:
(i) Anterior pituitary
(ii) Testes
(iii) Ovary
(iv) Adrenal cortex
(v) Pancreas
Make a table indicating the glands, hormones produced, their main functions and diseases caused due to their hypo and hypersecretions.
What do you mean by endocrine system?
Which parts of the alimentary canal produce hormones?
Differentiate: Hormones and Enzyme.
Differentiate: Insulin and Glucagon.
Give the Technical Term: Name two hormones secreted by the alimentary canal.
Give the Technical Term: Name a hormone which controls developments of male secondary sexual characters.
Give the Technical Term: The structure which controls the master gland.
Give the Technical Term: Name the glands which secrete the following hormone: Testosterone
Fill in the Blanks:
The glands with ducts are called ______.
The sketch below shows a certain condition in an individual:

(i) Name the condition.
(ii) What is the underlying cause of this condition?
(iii) Name two other conditions that could have resulted due to a similar cause.
(iv) Which hormone is required for iodine synthesis?
(v) Where is the thyroid gland located?
(vi) The hormone secreted by the thyroid gland is controlled from which hormone?
State the Function
Testosterone
Choose the Odd One Out
Choose the Odd One Out
Choose the Odd One Out
Choose the Odd One Out
Column ‘II’ is a list of items related to ideas in Column ‘I’. Match the term in Column ‘II’ with a suitable idea given in Column ‘I’.
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) Pituitary | (a) produces male sex characteristics |
| (ii) Ovaries | (b) decreases blood sugar level |
| (iii) Thyroid | (c) increases heart and breathing rate raises blood pressure |
| (iv) Thymus | (d) produces female sex characteristics |
| (v) Adrenals | (e) is known as emergency hormone |
| (vi) Hypothalamus | (f) regulates the level of calcium and phosphorus |
| (vii) Pancreas | (g) increases the rate of metabolism |
| (viii) Testes | (h) maintains the level of calcium |
| (ix) Parathyroid | regulates the amount of water excreted in the urine. |
| (x) Cretinism | (j) simulates skeletal growth |
| (xi) Diabetes mellitus | (k) regulates the activities of other glands |
| (xii) Insulin shock | (l) stimulates the development of male and female sex organs |
| (xiii) Gigantism | (m) Shortage of glucose in the blood. |
| (xiv) Enlargement of breasts in adult males | (n) Over-secretion of growth hormone |
| (xv) Exophthalmic goiter | (o) Excess of glucose in the blood |
| (xvi) Acromegaly | (p) Over-secretion of thyroxin |
| (xvii) Addison’s disease | (q) Dwarfism and mental retardation |
| (xviii)Cretinism | (r) Over-secretion of cortical hormones |
| (xix) Dwarfism | (s) Under-secretion of the adrenal cortex |
| (xx) Adrenalin | (t) Under-secretion of thyroxin in children |
| (xxi) Vasopressin | (u) Over-secretion of growth hormones in adults |
Which of the following are exclusive endocrine glands?
A pregnant female delivers a baby who suffers from stunted growth, mental retardation, low intelligence quotient and abnormal skin. This is the result of ______.
Write the role of oestrogen in ovulation?
Pineal gland is an endocrine gland, write its role.
Predict the effects of removal of pancreas from the human body.
Write a detailed account of gastro intestinal tract hormones.
In humans, the life processes are controlled and regulated by
