Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Compare the chemistry of actinoids with that of the lanthanoids with special reference to chemical reactivity.
उत्तर १
Generally, the initial members of the series are very reactive like calcium in their chemical behaviour, but with increasing atomic number they behave like aluminium.
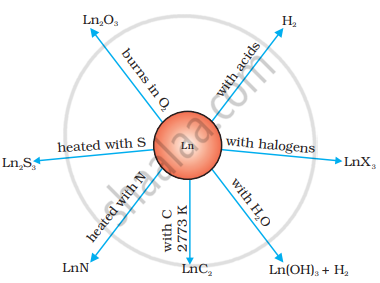
The value of EΘ for the half-reaction \[\ce{Ln^{3+}_{ (aq)} + 3e- -> Ln_{(s)}}\] is in the range of −2.2 V to −2.4 V. For Eu, the value of EΘ is −2.0 V. Of course, there is a slight variation in the value. These metals combine with hydrogen on being gently heated in an atmosphere of hydrogen gas. On heating these metals with carbon, the carbides Ln3C, Ln2C3 and LnC2 are formed. These metals liberate hydrogen gas from dilute acids and on burning in an atmosphere of halogens, form halides. These form oxide M2O3 and hydroxide M(OH)3. Hydroxides are definite compounds and not just hydrated oxides. They are basic, like the oxides and hydroxides of alkaline earth metals. Their general reactions are shown in the figure.
Actinoids are very reactive metals, especially when they are finely divided. The action of boiling water on them gives a mixture of oxide and hydride and combines with most non-metals at normal temperatures. Hydrochloric acid affects all metals, but most metals are little affected by nitric acid. The reason for this is that a protective surface of oxide is formed on these metals. Alkalis have no effect on these metals.
उत्तर २
Actinoids are far more reactive than lanthanoids. They interact with nonmetals at moderate temperatures. In contrast, lanthanoids react at high temperatures. The majority of actinoids are attacked by HNO3 has a small effect on HCl, although the creation of a protective layer of oxide. Alkalies cause no reaction. Lanthanoids extract hydrogen from dilute. Acids and halogens burn together to generate halides.
Notes
Students should refer to the answer according to their questions.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define lanthanoid contraction.
Write the different oxidation states of iron
What is lanthanoid contraction?
What are the consequences of lanthanoid contraction?
Account for the following:
Zn, Cd and Hg are soft metals.
What is Lanthanoid contraction?
Name an element of lanthanoid series which is well knwon to shown +4 oxidation state. Is it a strong oxidising agent or reducing agent?
What is lanthanoid contraction? Write the.............
What is meant by Lanthanide contraction? Write the general electronic configuration of inner transition elements.
The f-block elements are known as ____________.
Although +3 is the characteristic oxidation state for lanthanoids but cerium also shows +4 oxidation state because:
(i) it has variable ionisation enthalpy
(ii) it has a tendency to attain noble gas configuration
(iii) it has a tendency to attain f 0 configuration
(iv) it resembles Pb4+
Although +3 oxidation states is the characteristic oxidation state of lanthanoids but cerium shows +4 oxidation state also. Why?
Match the statements given in Column I with the oxidation states given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II | |
| (i) | Oxidation state of Mn in MnO2 is | (a) + 2 |
| (ii) | Most stable oxidation state of Mn is | (b) + 3 |
| (iii) | Most stable oxidation state of | (c) + 4 |
| Mn in oxides is | (d) + 5 | |
| (iv) | Characteristic oxidation state of lanthanoids is | (e) + 7 |
On the basis of Lanthanoid contraction, explain the following:
Trends in acidic character of lanthanoid oxides.
How would you account for the following:
There is a greater range of oxidation states among the actinoids than among the lanthanides.
Mischmetal is an alloy consisting mainly of ______.
Write a note on lanthanoids.
State a reason for the following:
La(OH)3 is more basic than Lu(OH)3.
