Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Compare the stability of +2 oxidation state for the elements of the first transition series.
उत्तर १
| Sc | +3 | ||||||
| Ti | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | |||
| V | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | ||
| Cr | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | |
| Mn | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 |
| Fe | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | |
| Co | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | ||
| Ni | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | |||
| Cu | +1 | +2 | +3 | ||||
| Zn | +2 |
From the above table, it is evident that the maximum number of oxidation states is shown by Mn, varying from +2 to +7. The number of oxidation states increases on moving from Sc to Mn. On moving from Mn to Zn, the number of oxidation states decreases due to a decrease in the number of available unpaired electrons. The relative stability of the +2 oxidation state increases on moving from top to bottom. This is because on moving from top to bottom, it becomes more and more difficult to remove the third electron from the d-orbital.
उत्तर २
Firstly, in the first half of the transition series, the sum of the first and second ionization enthalpies increases with increasing atomic number. Hence, the standard reducing potential (EΘ) is low and negative. Hence, the tendency to form M2+ ions decreases. Hence, the +2 oxidation state is more stable in the first half. The greater stability of the +2 oxidation state is due to half-filled d-subshells (d5) in Mn2+, fully filled d-subshells (d10) in Zn2+ and high negative hydration enthalpy in nickel.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why do interstitial compounds have higher melting points than corresponding pure metals?
Why do the transition elements have higher enthalpies of atomisation?
In 3d series (Sc to Zn), which element has the lowest enthalpy of atomisation and why?
How would you account for the following: Transition metals form complex compounds.
Account for the following:
E° value for the Mn3+/Mn2+ couple is much more positive than that for Cr3+/Cr2+.
What are the characteristics of the transition elements and why are they called transition elements?
Predict which of the following will be coloured in the aqueous solution?
Ti3+, V3+, Cu+, Sc3+, Mn2+, Fe3+ and Co2+. Give reasons for each.
What are alloys?
Compare the general characteristics of the first series of the transition metals with those of the second and third series metals in the respective vertical columns. Give special emphasis on the following point:
Electronic configurations
NF3 is possible, but NF5 is not. Why?
Account for the following :
Ti4+ is colourless whereas V4+ is coloured in an aqueous solutions.
Which among the following transition metal has the lowest melting point?
The magnetic moment is associated with its spin angular momentum and orbital angular momentum. Spin only magnetic moment value of \[\ce{Cr^{3+}}\] ion is ______.
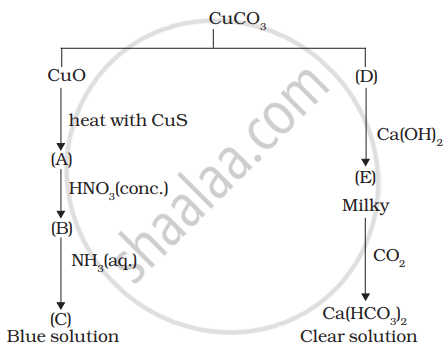
Identify A to E and also explain the reactions involved.
When a chromite ore (A) is fused with sodium carbonate in free excess of air and the product is dissolved in water, a yellow solution of compound (B) is obtained. After treatment of this yellow solution with sulphuric acid, compound (C) can be crystallised from the solution. When compound (C) is treated with KCl, orange crystals of compound (D) crystallise out. Identify A to D and also explain the reactions.
Answer the following question:
Which element of the first transition series has lowest enthalpy of atomisation?
Mention any three processes where transition metals act as catalysts.
Photographic film and plates have - au essential ingredient of
A complex in which dsp2 hybridisation takes place is
Give two similarities in the properties of Sc and Zn.
