Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
NF3 is possible, but NF5 is not. Why?
उत्तर
According to the electronic configuration of nitrogen, it does not have 3d orbital that's why it can't expand the valency up to 5 and does not form .
N does not have vacant d orbitals. Hence, there is no excitation of ns2 electron to vacant orbitals. Thus, has only three unpaired electrons in p-orbitals showing +3 oxidation state and not +5 in halides like other elements of group.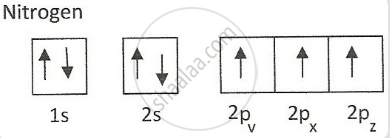
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which metal in the first transition series (3d series) exhibits + 1 oxidation state most frequently and why?
Account for the following:
Mn shows the highest oxidation state of +7 with oxygen but with fluorine, it shows oxidation state of +4.
Account for the following:
Cu+2 salts are coloured, while Zn2+ salts are white.
Why do the transition elements have higher enthalpies of atomisation?
Explain why Cu+ ion is not stable in aqueous solutions?
For M2+/M and M3+/M2+ systems, the EΘ values for some metals are as follows:
| Cr2+/Cr | −0.9 V |
| Mn2+/Mn | −1.2 V |
| Fe2+/Fe | −0.4 V |
| Cr3/Cr2+ | −0.4 V |
| Mn3+/Mn2+ | +1.5 V |
| Fe3+/Fe2+ | +0.8 V |
Use this data to comment upon:
The stability of Fe3+ in acid solution as compared to that of Cr3+ or Mn3+.
What are inner transition elements?
Write down the number of 3d electrons in the following ion:
Cu2+
Indicate how would you expect the five 3d orbitals to be occupied for this hydrated ions (octahedral).
Write the formula of an oxo-anion of Chromium (Cr) in which it shows the oxidation state equal to its group number
The transition metals show _________ character because of the presence of unpaired· electrons and Cu+ is ____________ because of its electronic configuration is [Ar]3d10
Transition metals with highest melting point is ____________.
Although Zirconium belongs to 4d transition series and Hafnium to 5d transition series even then they show similar physical and chemical properties because ______.
Why EΘ values for Mn, Ni and Zn are more negative than expected?
When a brown compound of manganese (A) is treated with \[\ce{HCl}\] it gives a gas (B). The gas taken in excess, reacts with \[\ce{NH3}\] to give an explosive compound (C). Identify compounds A, B and C.
Although fluorine is more electronegative than oxygen, but the ability of oxygen to stabilise higher oxidation states exceeds that of fluorine. Why?
Explain why does colour of \[\ce{KMNO4}\] disappear when oxalic acid is added to its solution in acidic medium.
EΘ of Cu is + 0.34V while that of Zn is – 0.76V. Explain.
The halides of transition elements become more covalent with increasing oxidation state of the metal. Why?
Answer the following question:
Which element of the first transition series has highest second ionisation enthalpy?
Account for the following:
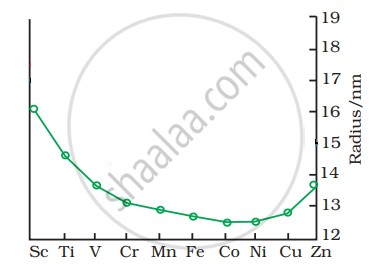
In case of transition elements, ions of the same charge in a given series show progressive decrease in radius with increasing atomic number.
On the basis of the figure given below, answer the following questions:
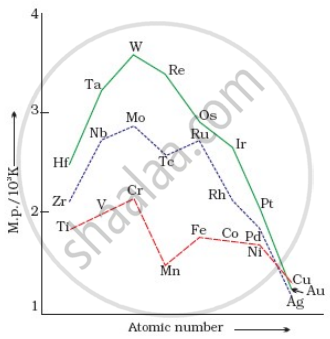
- Why Manganese has lower melting point than Chromium?
- Why do transition metals of 3d series have lower melting points as compared to 4d series?
- In the third transition series, identify and name the metal with the highest melting point.
On strong heating AgNO3, the gases evolved are:-
Sodium this sulphate is used in photography because of its:-
Give reason for the following statement:
Physical and chemical properties of the 4d and 5d series of the transition elements are quite similar to expected.
The oxidation state of Fe in [Fe(CO)5] is ______.
Account for the following:
Sc3+ is colourless whereas Ti3+ is coloured in an aqueous solution.
The given graph shows the trends in melting points of transition metals:

Explain the reason why Cr has the highest melting point and manganese (Mn) has a lower melting point.
Which of the following ions has the electronic configuration 3d6?
(Atomic number: Mn = 25, Co = 27, Ni = 28)
The trend of which property is represented by the following graph?