Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Predict which of the following will be coloured in the aqueous solution?
Ti3+, V3+, Cu+, Sc3+, Mn2+, Fe3+ and Co2+. Give reasons for each.
उत्तर १
Only the ions that have electrons in d-orbital and in which d-d transition is possible will be coloured. The ions in which d-orbitals are empty or completely filled will be colourless as no d-d transition is possible in those configurations.
| Element | Atomic Number | Ionic State | Electronic configuration in ionic state |
| Ti | 22 | Ti3+ | [Ar] 3d1 |
| V | 23 | V3+ | [Ar] 3d2 |
| Cu | 29 | Cu+ | [Ar] 3d10 |
| Sc | 21 | Sc3+ | [Ar] |
| Mn | 25 | Mn2+ | [Ar] 3d5 |
| Fe | 26 | Fe3+ | [Ar] 3d5 |
| Co | 27 | Co2+ | [Ar] 3d7 |
From the above table, it can be easily observed that only Sc3+ has an empty d-orbital and Cu+ has completely filled d-orbitals. All other ions, except Sc3+ and Cu+, will be coloured in aqueous solution because of d−d transitions.
उत्तर २
Those ions are coloured which have one or more unpaired electrons. Ti3+, V3+, Mn2+, Fe3+ and Co2+ are coloured. Cu+ and Sc3+ are colourless.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
ln which pair highest oxidation states of transition metals are found:
What are the transition elements? Write two characteristics of the transition elements.
Account for the following :
Zn is not considered as a transition element.
Complete and balance the following chemical equations
`Fe^(2+) + MnO_4^(-) + H^+ ->`
Why does the density of transition elements increase from Titanium to Copper? (at. no. Ti = 22,
Cu = 29)
Metallic radii of some transition elements are given below. Which of these elements will have highest density?
| Element | \[\ce{Fe}\] | \[\ce{Co}\] | \[\ce{Ni}\] | \[\ce{Cu}\] |
| Metallic radii/pm | 126 | 125 | 125 | 128 |
Match the catalysts given in Column I with the processes given in Column II.
| Column I (Catalyst) | Column II (Process) |
| (i) \[\ce{Ni}\] in the presence of hydrogen | (a) Zieglar Natta catalyst |
| (ii) \[\ce{Cu2C12}\] | (b) Contact process |
| (iii) \[\ce{V2O5}\] | (c) Vegetable oil to ghee |
| (iv) Finely divided iron | (d) Sandmeyer reaction |
| (v) \[\ce{TiCl4 + Al (CH3)3}\] | (e) Haber's Process |
| (f) Decomposition of KCIO3 |
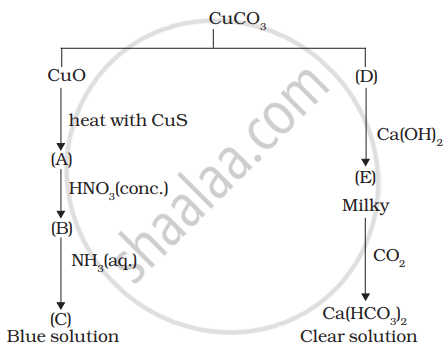
Identify A to E and also explain the reactions involved.
Identify the metal and justify your answer.
Carbonyl \[\ce{M(CO)5}\]
Why are fluorides of transition metals more stable in their higher oxidation state as compared to the lower oxidation state?
Which of the following maxm magnetic moment?
Why Zn, Cd and Hg are not called transition metals?
Consider the following standard electrode potentials (E° in volts) in aqueous solution:
| Element | M3+/M | M+/M |
| Al | - 1.66 | +0.55 |
| Tl | + 1.26 | -0.34 |
Based on these data, which of the following statements is correct?
The disproportionation of \[\ce{MnO^{2-}_4}\] in acidic medium resulted in the formation of two manganese compounds A and B. If the oxidation state of Mn in B is smaller than that of A, then the spin-only magnetic moment (µ) value of B in BM is ______. (Nearest integer)
Account for the following:
Ce4+ is a strong oxidising agent.
Which of the following ions has the electronic configuration 3d6?
(Atomic number: Mn = 25, Co = 27, Ni = 28)
The second ionization enthalpies of chromium and manganese are 1592 and 1509 kJ/mol respectively. Explain the lower value of Mn.
A pair of coloured ions is ______.
Decide which of the following atomic numbers are the atomic numbers of the inner transition elements:
29, 59, 74, 95, 102, 104
Compare the general characteristics of the first series of the transition metals with those of the second and third series metals in the respective vertical columns. Give special emphasis on the following point:
Ionisation enthalpies
