Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
[Cr(NH3)6]3+ is paramagnetic while [Ni(CN)4]2− is diamagnetic. Explain why?
उत्तर
Formation of [Cr(NH3)6]3+: The oxidation state of chromium in [Cr(NH3)6]3+ ion is +3. The electronic configuration of chromium is [Ar] 3d54s1. The hybridisation is shown in the following diagram –
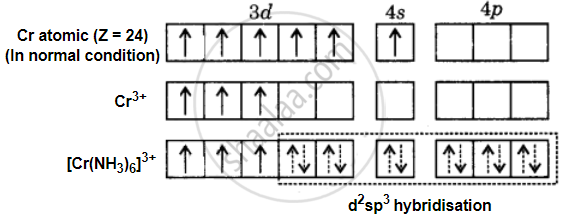
The Cr3+ ion provides six vacant orbitals to accommodate six electron pairs from six ammonia molecules. As a result, the complex [Cr(NH3)6]3+ has d2sp3 hybridisation and is octahedral. The presence of three unpaired electrons in the complex explains its paramagnetic property.
Formation of [Ni(CN)4]2−: In [Ni(CN)4]2− the oxidation state of Ni is +2 and its electronic configuration is 3d. Hybridisation can be explained as follows –
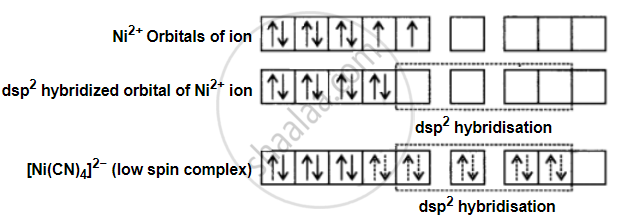
Each hybridised orbital accepts a pair of electrons from the cyanide ion. The absence of unpaired electrons confirms the diamagnetic behaviour of [Ni(CN)4]2−.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Predict the number of unpaired electrons in the square planar [Pt(CN)4]2− ion.
Discuss the nature of bonding in the following coordination entity on the basis of valence bond theory:
[Fe(CN)6]4−
Discuss the nature of bonding in the following coordination entity on the basis of valence bond theory:
[Co(C2O4)3]3−
Using valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the complexes given below:
\[\ce{[Co(NH3)6]^{3+}}\]
(i) Type of hybridisation.
(ii) Inner or outer orbital complex.
(iii) Magnetic behaviour.
(iv) Spin only magnetic moment value.
Using valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the complexes given below:
\[\ce{[Cr(H2O)6]^{3+}}\]
(i) Type of hybridisation.
(ii) Inner or outer orbital complex.
(iii) Magnetic behaviour.
(iv) Spin only magnetic moment value.
Using valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the complexes given below:
\[\ce{[FeCl6]^{4-}}\]
(i) Type of hybridisation.
(ii) Inner or outer orbital complex.
(iii) Magnetic behaviour.
(iv) Spin only magnetic moment value.
How many radial nodes for 3p orbital?
Which of the statement given below is incorrect about H2O2?
Which of the following has square planar structures?
In Fe(CO)5, the Fe – C bond possesses
Valence bond theory is based on the assumption that the bonds formed between the metal ions and ligands are ______
Using Valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the paramagnetic complex [Mn(CN)6]3-
- type of hybridization
- magnetic moment value
- type of complex – inner, outer orbital complex
Using valence bond theory, predict the hybridization and magnetic character of the following:
[CoF6]3– [Atomic number of Co = 27]
Write the hybridisation and magnetic behaviour of [CoF6]3−.
[Given: Atomic number of Co = 27]
