Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
[Cr(NH3)6]3+ is paramagnetic while [Ni(CN)4]2− is diamagnetic. Explain why?
उत्तर
Formation of [Cr(NH3)6]3+: The oxidation state of chromium in [Cr(NH3)6]3+ ion is +3. The electronic configuration of chromium is [Ar] 3d54s1. The hybridisation is shown in the following diagram –
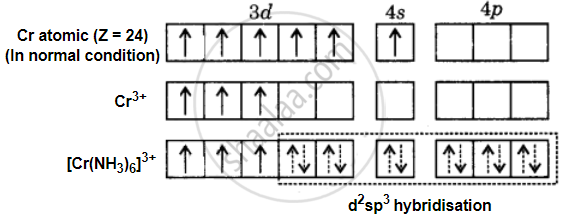
The Cr3+ ion provides six vacant orbitals to accommodate six electron pairs from six ammonia molecules. As a result, the complex [Cr(NH3)6]3+ has d2sp3 hybridisation and is octahedral. The presence of three unpaired electrons in the complex explains its paramagnetic property.
Formation of [Ni(CN)4]2−: In [Ni(CN)4]2− the oxidation state of Ni is +2 and its electronic configuration is 3d. Hybridisation can be explained as follows –
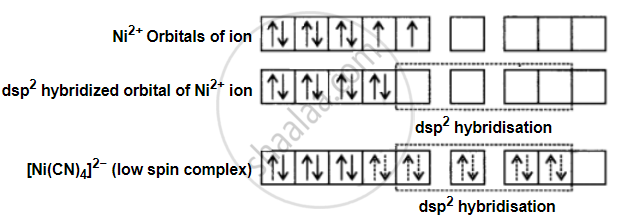
Each hybridised orbital accepts a pair of electrons from the cyanide ion. The absence of unpaired electrons confirms the diamagnetic behaviour of [Ni(CN)4]2−.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Discuss the nature of bonding in the following coordination entity on the basis of valence bond theory:
[Fe(CN)6]4−
Discuss the nature of bonding in the following coordination entity on the basis of valence bond theory:
[FeF6]3−
[NiCl4]2- is paramagnetic while [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic though both are tetrahedral. Why? (Atomic no. Ni = 28)
Using valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the complexes given below:
\[\ce{[Mn(CN)6]^{3-}}\]
(i) Type of hybridisation.
(ii) Inner or outer orbital complex.
(iii) Magnetic behaviour.
(iv) Spin only magnetic moment value.
Using valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the complexes given below:
\[\ce{[Co(NH3)6]^{3+}}\]
(i) Type of hybridisation.
(ii) Inner or outer orbital complex.
(iii) Magnetic behaviour.
(iv) Spin only magnetic moment value.
Using valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the complexes given below:
\[\ce{[Cr(H2O)6]^{3+}}\]
(i) Type of hybridisation.
(ii) Inner or outer orbital complex.
(iii) Magnetic behaviour.
(iv) Spin only magnetic moment value.
The type of hybridization involved in Octahedral complexes is ______.
Write the hybridization and shape of the following complexes:
[Ni(CN)4]2−
In a coordination entity, the electronic configuration of the central metal ion is t2g3 eg1
Is the coordination compound a high spin or low spin complex?
Which of the statement given below is incorrect about H2O2?
What is the no. of possible isomers for the octahedral complex [Co(NH3)2(C2O4)2]?
Using valence bond theory, predict the hybridization and magnetic character of the following:
[CoF6]3– [Atomic number of Co = 27]
Write the hybridisation and magnetic behaviour of [CoF6]3−.
[Given: Atomic number of Co = 27]
[Ni(CO)4] has tetrahedral geometry while [Ni(CN)4]2− has square planar, yet both exhibit diamagnetism. Explain.
[Atomic number: Ni = 28]
During chemistry class, a teacher wrote \[\ce{[Ni(CN)4]^2-}\] as a coordination complex ion on the board. The students were asked to find out the magnetic behaviour and shape of the complex. Pari, a student, wrote the answer paramagnetic and tetrahedral whereas another student Suhail wrote diamagnetic and square planer.
Evaluate Pari’s and Suhail’s responses.
