Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
[Ni(CO)4] has tetrahedral geometry while [Ni(CN)4]2− has square planar, yet both exhibit diamagnetism. Explain.
[Atomic number: Ni = 28]
उत्तर
In [Ni(CN)4]2−, nickel is in a +2 oxidation state and the ion has the electronic configuration 3d8. The hybridisation scheme is shown in the diagram.
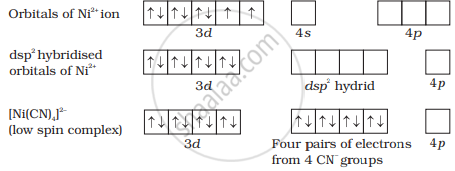
Whereas in [Ni(CO)4], Ni is in a +2 oxidation state and shows sp2 hybridisation due to which its geometry is tetrahedral.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Discuss the nature of bonding in the following coordination entity on the basis of valence bond theory:
[Co(C2O4)3]3−
Write the hybridisation and number of unpaired electrons in the complex `[CoF_6]^(3-)`. (Atomic No. of Co = 27)
[NiCl4]2- is paramagnetic while [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic though both are tetrahedral. Why? (Atomic no. Ni = 28)
Using valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the complexes given below:
\[\ce{[Co(NH3)6]^{3+}}\]
(i) Type of hybridisation.
(ii) Inner or outer orbital complex.
(iii) Magnetic behaviour.
(iv) Spin only magnetic moment value.
Using valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the complexes given below:
\[\ce{[FeCl6]^{4-}}\]
(i) Type of hybridisation.
(ii) Inner or outer orbital complex.
(iii) Magnetic behaviour.
(iv) Spin only magnetic moment value.
How many radial nodes for 3p orbital?
Which of the following methods is used for measuring bond length?
In Fe(CO)5, the Fe – C bond possesses
Using Valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the paramagnetic complex [Mn(CN)6]3-
- type of hybridization
- magnetic moment value
- type of complex – inner, outer orbital complex
The magnetic moment of [NiCl4]2− is ______.
[Atomic number: Ni = 28]
