Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
[Ni(CO)4] has tetrahedral geometry while [Ni(CN)4]2− has square planar, yet both exhibit diamagnetism. Explain.
[Atomic number: Ni = 28]
उत्तर
In [Ni(CN)4]2−, nickel is in a +2 oxidation state and the ion has the electronic configuration 3d8. The hybridisation scheme is shown in the diagram.
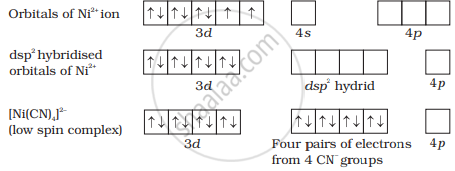
Whereas in [Ni(CO)4], Ni is in a +2 oxidation state and shows sp2 hybridisation due to which its geometry is tetrahedral.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
[NiCl4]2− is paramagnetic, while [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic, though both are tetrahedral. Why? (Atomic number of Ni = 28)
Explain on the basis of valence bond theory that [Ni(CN)4]2− ion with square planar structure is diamagnetic and the [NiCl4]2− ion with tetrahedral geometry is paramagnetic.
Predict the number of unpaired electrons in the square planar [Pt(CN)4]2− ion.
Discuss the nature of bonding in the following coordination entity on the basis of valence bond theory:
[Fe(CN)6]4−
Discuss the nature of bonding in the following coordination entity on the basis of valence bond theory:
[FeF6]3−
The type of hybridization involved in Octahedral complexes is ______.
Which of the statement given below is incorrect about H2O2?
When the hybridization state of carbon changes from sp3 to sp2 and finally to sp, the angle between hybridized orbital will
What is the no. of possible isomers for the octahedral complex [Co(NH3)2(C2O4)2]?
Using Valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the paramagnetic complex [Mn(CN)6]3-
- type of hybridization
- magnetic moment value
- type of complex – inner, outer orbital complex
