Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define ionisation enthalpy. Discuss the factors affecting ionisation enthalpy of the elements and its trends in the periodic table.
उत्तर
The amount of energy required to remove an electron from the outermost shell of an isolated gaseous atom in its ground state is said to be ionisation enthalpy.
The factors that affect ionization enthalpy of the elements are as follows:
a. Effective nuclear charge with its increase the ionization enthalpy also increases
b. Atomic size with its increase the ionization enthalpy decreases
c. The \[\ce{e- - e-}\] repulsion with its increase the ionization enthalpy decreases
d. Whenever there exists half-filled or completely filled orbital than it lead to increase the ionization enthalpy because it leads to give extra stability to the atom due to symmetry
The ionization enthalpy decreases down the group and increases across the period.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Energy of an electron in the ground state of the hydrogen atom is –2.18 × 10–18 J. Calculate the ionization enthalpy of atomic hydrogen in terms of J mol–1.
Hint: Apply the idea of mole concept to derive the answer.
Among the second period elements the actual ionization enthalpies are in the
order Li < B < Be < C < O < N < F < Ne.
Explain why O has lower ΔiH than N and F?
Which one of the following statements is incorrect in relation to ionization enthalpy?
Nitrogen has positive electron gain enthalpy whereas oxygen has negative. However, oxygen has lower ionisation enthalpy than nitrogen. Explain.
Arrange the elements \[\ce{N, P, O}\] and \[\ce{S}\] in the order of increasing first ionisation enthalpy. Give reason for the arrangement assigned.
Explain the deviation in ionisation enthalpy of some elements from the general trend by using the given figure.
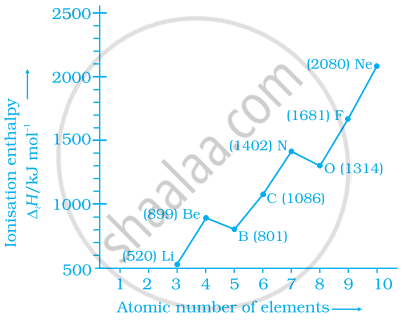
Discuss and compare the trend in ionisation enthalpy of the elements of group1 with those of group17 elements.
Consider the elements Mg, Al, S, P and Si, the correct increasing order of their first ionization enthalpy is ______.
For the gaseous reaction, \[\ce{K_{(g)} + F_{(g)} -> K^+_{ (g)} + F^-_{ (g)}}\], ΔH was calculated to be 19 kcal/mol under conditions where the cations and anions were prevented by electrostatic separation from combining with each other. The ionisation energy of K is 4.3 eV. The electron affinity of F is ______. (in eV)
Which of the following atoms has the highest first ionization energy?
