Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
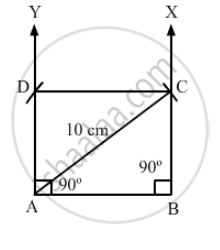
Draw a rectangle whose one side measures 8 cm and the length of each of whose diagonals is 10 cm.
उत्तर
(i) Draw a side AB, equal to 8 cm.
(ii) With A as the centre, draw an arc of length 10 cm.
(iii) Draw\[\angle\]ABX = 90° which intersects the arc at C.
(iv)Draw\[\angle\]= 90° .
(v) With C as the centre, draw an arc of length 8 cm.
(vi) Join CD.
Thus, ABCD is the required rectangle.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In Fig. 17.29, suppose it is known that DE = DF. Then, is ΔABC isosceles? Why or why not?
Which of the following statement is true for a rectangle?
It has all its sides of equal length.
Which of the following statement are true for a square?
It has all its sides of equal length.
Find the length of the diagonal of a rectangle whose sides are 12 cm and 5 cm.
Draw a rectangle ABCD such that l(AB) = 6.0 cm and l (BC) = 4.5 cm.
The interior angle made by the side in a parallelogram is 90° then the parallelogram is a
If the diagonals of a quadrilateral are equal and bisect each other, then the quadrilateral is a ______.
Every parallelogram is a rectangle.
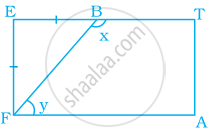
A playground is in the form of a rectangle ATEF. Two players are standing at the points F and B where EF = EB. Find the values of x and y.
Quadrilateral EFGH is a rectangle in which J is the point of intersection of the diagonals. Find the value of x if JF = 8x + 4 and EG = 24x – 8.
