Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw the plot of amplitude versus ‘ω’ for an amplitude modulated wave whose carrier wave (ωc) is carrying two modulating signals, ω1 and ω2 (ω2 > ω1).
- Is the plot symmetrical about ωc? Comment especially about plot in region ω < ωc.
- Extrapolate and predict the problems one can expect if more waves are to be modulated.
- Suggest solutions to the above problem. In the process can one understand another advantage of modulation in terms of bandwidth?
उत्तर
`v(t) = A(A_(m_1) sin ω_(m_1) t + A_(m_2) sinω_(m_2) t + A_c sin ω_c t) + B(A_(m_1) sin ω_(m_1) t + A_(m_2) t + A_c sinω_ct)^2`
= `A(A_(m_1) sin ω_(m_1) t + A_(m_2) sin ω_(m_2) t + A_c sin ω_ct)^2 + B((A_(m_1) sin ω_(m_1) t + A_(m_2) t)^2 + A_c^2 sin^2 ω_ct + 2A_c (A_(m_1) sinω_(m_1) t + A_(m_2) sin ω_c t)`
= `A(A_1 sin ω_(m_1) t + A_(m_2) sin ω_(m_2) t + A_c sin ω_ct) + B[A_(m_1^2) sin^2 ω_(m_1) t + A_(m_2)^2 sin^2 ω_(m_2)t + 2A_(m_1) A_(m_2) sin ω_(m_1) t sin ω_(m_2)t + A_c^2 sin^2 ω_ct + 2A_c (A_(m_1) sin ω_(m_1) t sin ω_ct + A_(m_2) sin ω_(m_2) + sin ω_ct]`
= `A(A_(m_1) sin ω_(m_1) t + A_(m_2) sin ω_(m_2) t + A_c sin ω_c t + B[A_(m_1)^2 sin^2 ω_(m_1) t + A_(m_2)^2 sin^2 ω_(m_2) t + A_c^2 sin^2 ω_c t + (2A_(m_1) A_(m_2))/2 [cos (ω_(m_2) - ω_(m_1))t - cos(ω_(m_1) + ω_(n_2))t] + (2A_c A_(m_2))/2 [cos(ω_c - ω_(m_1))t - cos[ω_c + ω_(m_1))t + (2A_cA_(m_1))/2 [cos(ω_c - ω_(m_2))t - cos(ω_c + ω_(m_2))t]]`
∴ Frequencies present are `ω_(m_1), ω_(m_2), ω_(ω_c)`
`(ω_(m_1) - ω_(m_1)), (ω_(m_1) + ω_(m_2))`
`(ω_c - ω_(m_1)), (ω_c + ω_(m_1))`
`(ω_c - ω_(m_2)), (ω_c + ω_(m_2))`
i. Plot of amplitude versus ω is shown in the Figure.
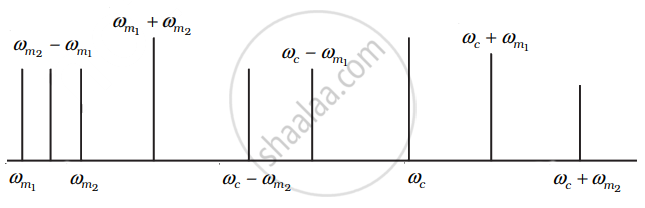
ii. As can be seen frequency spectrum is not symmetrical about ωc. Crowding of the spectrum is present for ω < ωc.
iii. Adding more modulating signals lead to more crowding in ω < ωc and more chances of mixing of signals.
iv. Increase bandwidth and ωc to accommodate more signals. This shows that a large carrier frequency enables to carry more information (more ωm) and which will in turn increase bandwidth.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
For an amplitude modulated wave, the maximum amplitude is found to be 10 V while the minimum amplitude is found to be 2 V. Determine the modulation index μ. What would be the value of μ if the minimum amplitude is zero volt?
How is amplitude modulation achieved?
Explain any two factors which justify the need for modulating a low frequency base-band signal.
Write three important factors which justify the need of modulating a message signal. Show diagrammatically how an amplitude modulated wave is obtained when a modulating signal is superimposed on a carrier wave.
What is meant by term ‘modulation’? Draw a block diagram of a simple modulator for obtaining an AM signal.
Define amplitude modulation in a communication system.
A message signal of frequency ωm is superposed on a carrier wave of frequency ωc to get an amplitude modulated wave (AM). The frequency of the AM wave will be ______.
The maximum amplitude of an A.M. wave is found to be 15 V while its minimum amplitude is found to be 3 V. What is the modulation index?
Why is a AM signal likely to be more noisy than a FM signal upon transmission through a channel?
The maximum amplitude for an amplitude modulated wave is found to be 12V while the minimum amplitude is found to be 3V. The modulation index is 0.6x where x is ______.
