Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain aqueous alkaline hydrolysis of tert. butyl bromide.
उत्तर
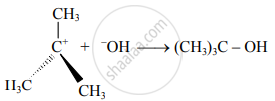
i. Aqueous alkaline hydrolysis of tert. butyl bromide forms tert-butyl alcohol. The reaction can be given as,
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{\phantom{....}CH3\phantom{.........................}}\ce{CH3\phantom{............}}\\
|\phantom{.............................}|\phantom{...........}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - Br +\underset{\text{Nucleophile}}{OH-} ->CH3 - C - OH +\underset{\text{Bromide ion}}{Br-}}\\
|\phantom{.............................}|\phantom{...........}\\
\ce{\underset{\text{Tert-Butyl bromide}}{CH3}\phantom{.................}}
\ce{\underset{\text{tert−Butyl alcohol}}{CH3}}\phantom{.........}\\
\end{array}\]
Rate = k [(CH3)3C − Br]
ii. The reaction follows the first-order kinetics. That is, the rate of this reaction depends on the concentration of only one species, which is the substrate molecule, tert-butyl bromide. Hence, it is called substitution nucleophilic unimolecular, SN1 mechanism.
iii. It can be seen in the reaction that the concentration of the only substrate appears in the rate equation that is, the concentration of the nucleophile does not influence the reaction rate.
iv. In other words, tert-butyl bromide reacts with hydroxide by a two steps mechanism.
In the slow step C–X bond in the substrate undergoes heterolysis and in the subsequent fast step, the nucleophile uses its electron pair to form a new bond with the carbon undergoing change.
v. The SN1 mechanism is represented as,
- Step I:

- Step II:
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
from the following pair would undergo SN2 faster from the other?
a. ![]() b.
b. ![]()
Complete the following reaction giving major products.
\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3 - CH - CH3 ->[Red P/Br2] A ->[Ag2O/H2O]B}\\|\phantom{.........................}\\
\ce{OH\phantom{.......................}}\end{array}\]
Complete the following reaction giving major product.
\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3\phantom{................}}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH2 - Cl ->[Na/dry ether] A}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3\phantom{................}}
\end{array}\]
Name the reagent used to bring about the following conversion.
Chlorobenzene to biphenyl
Arrange the following in the increasing order of boiling points.
- 1-Bromopropane
- 2- Bromopropane
- 1- Bromobutane
- 1-Bromo-2-methylpropane
Give reasons:
Haloarenes are less reactive than haloalkanes.
HCl is added to a hydrocarbon ‘A’ \[\ce{(C4H8)}\] to give a compound ‘B’ which on hydrolysis with aqueous alkali forms tertiary alcohol ‘C’ \[\ce{(C4H10O)}\]. Identify ‘A’ ,‘B’ and ‘C’.
Observe the following and answer the question given below.

Name the type of halogen derivative.
Observe the following and answer the question given below.

Comment on the bond length of C–X bond in it.
Write the correct order of increasing ease of dehydrohalogenation.
\[\ce{\underset{\text{(I)}}{CH3 - CH2 - CH2 - Cl}}\]
\[\ce{\underset{\text{(II)}}{CH3 - CH(Cl) - CH3}}\]
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\\
|\\
\ce{CH3-C-Cl}\phantom{...}\\
|\\
\ce{CH3}\\
\ce{(III)}
\end{array}\]
Explain. Aryl halides are less reactive than alkyl halides towards nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Explain primary benzylic halide shows higher reactivity by SN1 mechanism than other primary alkyl halide.
In alkaline hydrolysis of tertiary butyl bromide, ____________.
Nitroalkanes are obtained in laboratory from primary or secondary alkyl halides by the action of ______.
\[\ce{C6H5CH2Cl + KCN(alc) -> X + Y}\]
Compounds X and Y are ____________.
The SN2 reaction of a compound containing an asymmetric carbon atom always gives ____________.
Identify major product 'B' in the following reaction.
\[\ce{But-1-ene ->[HBr][Peroxide] A ->[AgCN][\Delta] B}\]
Write the product formed when alkyl halide reacts with silver nitrite.
The order of reactivity of the given haloalkanes towards nucleophiles is:
With which halogen the reactions, of alkanes are explosive?
The compound that reacts the fastest with sodium methoxide is ______.
Complete the following reaction giving major products.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.......}\\
|\phantom{.........}\\
\ce{CH3 - c - CH2 - Cl ->[Na/dry ether]}\\
|\phantom{.........}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.......}
\end{array}\]
Observe the following and answer the question given below:
Comment on the bond length of C-X bond in it.
Complete the following reaction sequences by writing the structural formulae of the organic compounds 'A', 'B' and 'C'.
\[\ce{2-Bromobutan ->[alc. KOH] A ->[][Br2] B ->[][NANH2] C}\]
Complete the following reaction giving major product.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{...............}\\
|\phantom{..................}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH2 - Cl->[Na/dry ether]A}\\
|\phantom{..................}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{...............}\\
\end{array}\]
Complete the reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2Cl ->[AgCN][alc.\Delta]}\] ?
Complete the following reaction giving major product.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{...............}\\
|\phantom{..................}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH2 - Cl ->[Na/dry ether]A}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.................}
\end{array}\]
Give a reason for the following:
Ethoxy ethane with conc. HI at 373 K gives C2H5OH and CH3I but not CH3OH and C2H5I.
