Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the factors affecting SN1 and SN2 mechanism.
उत्तर
Factors that affect the SN1 and SN2 mechanisms:
- Nature of substrate
- Nucleophilicity of the reagent
- Solvent polarity
i. Nature of substrate:
- SN2 mechanism: The transition state (T.S.) of the SN2 mechanism is pentacoordinate and thus crowded. As a result, SN2 mechanism is favoured in primary halides and least favoured in tertiary halides. Reactivity order of alkyl halides towards SN2 mechanism: 3° < 2° < 1°< CH3X.
- SN1 mechanism: A planar carbocation intermediate is formed in the SN1 reaction. It has no steric crowding as bulky alkyl groups can be easily accommodated in planar carbocation.
Formation of planar carbocation intermediate results in a relief from steric crowding present in the tertiary halide substrate.
Secondly, the carbocation intermediate is stabilized by +I effect of alkyl substituents and by the hyperconjugation effect of alkyl substituents containing α-hydrogens.
As a result, SN1 mechanism is most favoured in tertiary halides and least favoured in primary halides.
Reactivity order of alkyl halides towards SN1 mechanism: 3° > 2° > 1°> CH3X.
ii. Nucleophilicity of the reagent:
- SN2 mechanism: A more powerful nucleophile attacks the substrate faster and favours the SN2 mechanism.
- SN1 mechanism: The rate of the SN1 mechanism is independent of the nature of nucleophile as nucleophile does not react in the slow step of SN1. It waits till the carbocation intermediate is formed, and reacts fast with it.
iii. Solvent polarity:
- SN2 mechanism: Polar protic solvents usually decrease the rate of an SN2 reaction. In the rate-determining step of the SN2 mechanism, the substrate, as well as nucleophile, is involved.
A polar solvent stabilizes nucleophile (one of the reactants) by solvation. Thus, solvent deactivates the nucleophile by stabilizing it. Hence, aprotic solvents or solvents of low polarity will favour the SN2 mechanism. - SN1 mechanism: SN1 mechanism proceeds via the formation of a carbocation intermediate. A good ionizing solvent, polar solvent, stabilizes the ions by solvation.
Solvation of carbocation is relatively poor and solvation of anion is particularly important. Anions are solvated by hydrogen-bonding solvents, that is, protic solvents.
Thus, the SN1 reaction proceeds more rapidly in polar protic solvents than in aprotic solvents.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Complete the following reaction giving major products.
\[\ce{CH3 - CH = CH2 ->[HBr][peroxide] A ->[alc. KOH] B}\]
Complete the following reaction giving major products.
\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3 - CH - CH3 ->[Red P/Br2] A ->[Ag2O/H2O]B}\\|\phantom{.........................}\\
\ce{OH\phantom{.......................}}\end{array}\]
Complete the following reaction giving major product.
\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3\phantom{................}}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH2 - Cl ->[Na/dry ether] A}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3\phantom{................}}
\end{array}\]
Name the reagent used to bring about the following conversion.
Bromoethane to ethoxyethane
Name the reagent used to bring about the following conversion.
1-Chloropropane to 1-nitropropane
Distinguish between SN1 and SN2 mechanism of substitution reaction.
Convert the following:
Ethanol to propane nitrile
Complete the following reaction sequence by writing the structural formulae of the organic compound 'A', 'B' and 'C'.
\[\ce{2-Bromobutane->[Alc.KOH]A->[][Br2]B->[][NaNH2]C}\]
Complete the following reaction sequence by writing the structural formulae of the organic compound 'A', 'B' and 'C'.
\[\ce{Isopropyl alcohol ->[\triangle][PBr3] A ->[][NH3 excess] B}\]
What is dehydrohalogenation? State the rule for the formation of the preferred product of dehydrohalogenation.
Which of the following is least reactive towards SN1 reactions?
Ethyl bromide undergoes the following reaction:
\[\ce{\underset{Ethyl bromide}{C2H5Br} + \underset{(aq.)}{KOH} ->[\Delta] \underset{Ethyl alcohol}{C2H5OH} + KBr}\]
Which of the following is a WRONG statement?
Dehydrohalogenation of an alkyl halide is ____________.
Which one is most reactive towards nucleophilic addition reaction?
What type of hybridisation is present in carbocation formed during the alkaline hydrolysis of 1- bromo-1- phenyl ethane?
What is the major product obtained in the sulphonation of chlorobenzene with concentrated sulphuric acid?
Convert the following.
p-Nitrochlorobenzene to p-nitrophenol
The major product formed when 2-bromobutane is treated with alcoholic KOH is ______.
The order of reactivities of the following alkyl halides for an SN2 reaction is ______.
Which among the following statements is not correct about SN2 reaction mechanism?
The compound that reacts the fastest with sodium methoxide is ______.
Complete the following reaction giving major products.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.......}\\
|\phantom{.........}\\
\ce{CH3 - c - CH2 - Cl ->[Na/dry ether]}\\
|\phantom{.........}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.......}
\end{array}\]
Complete the following reactions giving a major product.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{................}\\
|\phantom{..................}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH2 - Cl ->[Na/dry ether] A}\\
|\phantom{..................}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{................}
\end{array}\]
Observe the following and answer the question given below:
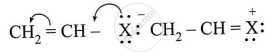
Comment on the bond length of C-X bond in it.
Observe the following and answer the question given below:
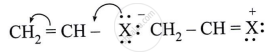
Can react by SN1 mechanism? Justify your answer.
Complete the following reactions giving major product.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{................}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH2 - Cl ->[Na/dry ether] A}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.................}
\end{array}\]
